Currency Pairs in Forex Trading
Currency pairs are the cornerstone of forex trading, representing the exchange rate between two different currencies. Each pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency, with the base currency being the one that is being bought or sold. For instance, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro (EUR) is the base currency and the US dollar (USD) is the quote currency. This means that the EUR/USD rate tells traders how many US dollars are needed to purchase one euro. Understanding these pairs is essential for navigating the forex market, as they are the fundamental units of currency exchange and trading.
In the forex market, currency pairs are categorized into major, minor, and exotic pairs. Major pairs, like EUR/USD and USD/JPY, are the most traded and offer high liquidity and lower volatility. Minor pairs, such as EUR/GBP and GBP/JPY, do not include the US dollar but involve other major currencies. Exotic pairs, including USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira) and USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South African Rand), combine one major currency with one from an emerging or smaller economy, offering potential for higher volatility and trading opportunities. Mastering the dynamics of these currency pairs and understanding the factors that influence their fluctuations is crucial for any successful forex trader.
Contents
What is a Currency Pair?
Definition and Structure
A currency pair is essentially a way of quoting how one currency is valued against another. It consists of two currencies: the base currency and the quote currency. The base currency is listed first, and the quote currency is listed second. For instance, in the EUR/USD pair, EUR is the base currency, and USD is the quote currency. This pair tells us how much of the quote currency (USD) is needed to buy one unit of the base currency (EUR).
Imagine you’re in a bustling international market, and you need to exchange euros for dollars. The EUR/USD rate you see will tell you how many dollars you’ll get for each euro. This exchange rate is constantly fluctuating due to various market forces.

How Currency Pairs Work
When you buy a currency pair, you’re effectively buying the base currency and selling the quote currency. Conversely, selling the pair means selling the base currency and buying the quote currency. This dynamic creates a global marketplace where currencies are continuously traded, with their values determined by supply and demand.
For instance, if you believe the euro will strengthen against the dollar, you might buy EUR/USD. If the euro does appreciate, you could sell it later at a higher price, profiting from the change. It’s like betting on which currency will perform better against the other.
Importance of Currency Pairs
Facilitating Global Trade and Investment
Currency pairs are vital for global trade and investment. They provide a standardized method to compare the values of different currencies, making it easier for businesses and individuals to exchange money across borders. Whether you’re a multinational corporation dealing with international clients or a traveler needing local currency, understanding currency pairs is essential.
Think of currency pairs as a universal translator for money. Without them, international transactions would be cumbersome and prone to errors. By using currency pairs, businesses can price their products accurately and individuals can make informed decisions about their foreign transactions.
Opportunities for Speculation
Besides facilitating trade, currency pairs offer significant opportunities for speculation. The forex market is one of the largest and most liquid financial markets in the world, allowing traders to profit from fluctuations in currency values. The ability to trade on margin means that even small price movements can lead to substantial profits—or losses.
Consider this: You might speculate that the British pound will rise against the US dollar due to positive economic news from the UK. By buying GBP/USD, you stand to benefit if the pound does indeed appreciate. However, this potential for profit comes with the risk of significant losses, emphasizing the importance of understanding how currency pairs work.

Major Currency Pairs
Overview
Major currency pairs are the most traded in the forex market. They involve the most economically significant and stable countries and always include the US dollar (USD) on one side. These pairs are known for their high liquidity, tight spreads, and generally lower volatility compared to other pairs.
Why is the US dollar so dominant in these pairs? It’s because the US dollar serves as the world’s primary reserve currency, used in most global transactions and financial reserves. This dominance makes major pairs highly liquid, meaning they can be bought or sold with minimal impact on their price.
Examples of Major Currency Pairs
Here are some of the key major currency pairs you might encounter:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar): Represents the Eurozone against the US dollar.
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen): Reflects the value of the dollar against the yen.
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar): Shows how the pound compares to the dollar.
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc): Compares the dollar to the Swiss franc.
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar): Measures the Australian dollar against the US dollar.
- USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar): Compares the dollar to the Canadian dollar.
EUR/USD: The Most Traded Pair
The EUR/USD pair is the most traded currency pair in the forex market. It represents the Eurozone and the United States, two of the world’s largest economic regions. The high liquidity and narrow spreads of this pair make it a favorite among traders.
Case Study: Trading EUR/USD
Imagine you’re a trader who anticipates the US economy will outperform the Eurozone due to strong economic reports. You might decide to sell EUR/USD, expecting the euro to weaken against the dollar. If your prediction is correct and the euro does fall, you could buy it back at a lower price, making a profit from the difference.
In my early trading days, I remember a particular instance where the US had robust job growth figures. I anticipated this would strengthen the USD against the EUR. By carefully analyzing the economic data and market sentiment, I managed to profit from this move, reinforcing the importance of staying informed about economic indicators.
USD/JPY: A Popular Pair in Asia
The USD/JPY pair involves the US dollar and the Japanese yen. Known for its liquidity and sensitivity to geopolitical events, this pair is frequently used by traders to exploit interest rate differentials between the US and Japan.
Personal Experience:
I vividly recall focusing on the USD/JPY pair during a period of heightened geopolitical tension in Asia. By monitoring news reports and economic data closely, I was able to predict a significant movement in the pair, resulting in a successful trade. This experience underscored the importance of staying updated on global events.
Minor Currency Pairs
Overview
Minor currency pairs, or cross-currency pairs, do not include the US dollar. These pairs involve combinations of major currencies like the euro, British pound, and Japanese yen. While they are less liquid than major pairs and often have wider spreads, they offer additional trading opportunities.
Why trade minor pairs? They provide diversification opportunities and can react differently to global events compared to major pairs, allowing traders to capitalize on various market conditions.
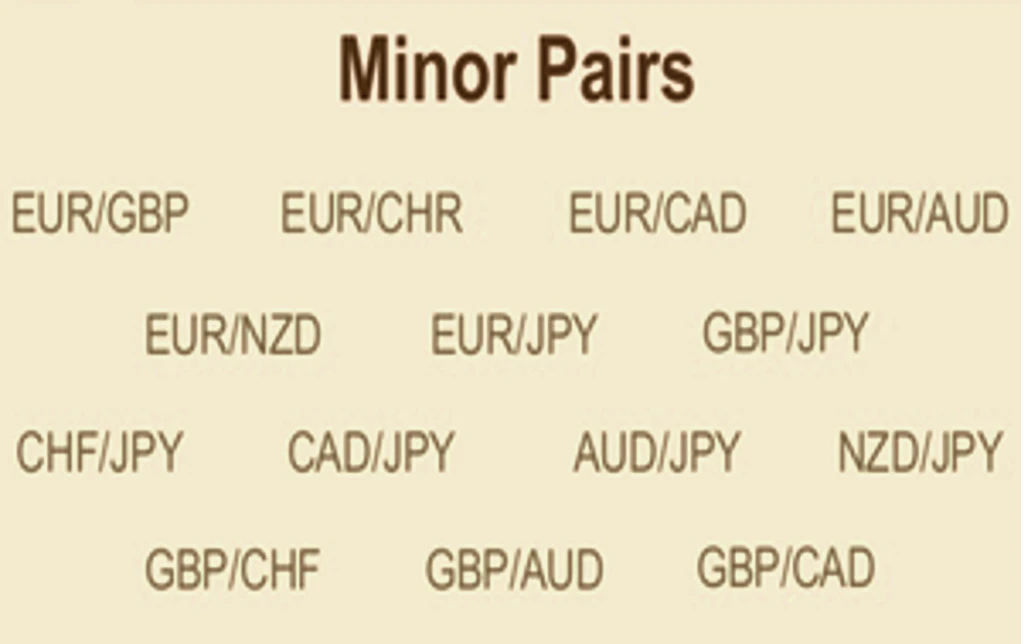
Examples of Minor Currency Pairs
Here are a few notable minor currency pairs:
- EUR/GBP (Euro/British Pound): Reflects the value of the euro against the pound.
- EUR/JPY (Euro/Japanese Yen): Measures the euro’s value relative to the yen.
- GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen): Compares the pound to the yen.
- AUD/NZD (Australian Dollar/New Zealand Dollar): Shows the relationship between the Australian and New Zealand dollars.
- EUR/CHF (Euro/Swiss Franc): Reflects the euro’s value against the Swiss franc.
EUR/GBP: Reflecting European Economies
The EUR/GBP pair shows the economic relationship between the Eurozone and the UK. It is influenced by data and events from both regions. For example, Brexit negotiations had a notable impact on this pair, creating opportunities for traders.
Case Study: Trading EUR/GBP
Suppose you believe the Eurozone will outperform the UK due to stronger economic growth. In that case, you might buy EUR/GBP, anticipating that the euro will strengthen relative to the pound. If your analysis is correct, the euro’s appreciation could lead to profits from the pair’s price movement.
Personal Insight:
I once traded the EUR/GBP pair during a period of uncertainty surrounding Brexit. By analyzing the political developments and economic reports, I was able to anticipate significant volatility and capitalize on it. This experience highlighted the importance of staying informed about geopolitical events.
EUR/JPY: Combining Europe and Asia
The EUR/JPY pair involves the euro and the Japanese yen, reflecting economic ties between Europe and Asia. It is sensitive to economic indicators and geopolitical events in both regions. Traders often use this pair to diversify their portfolios and take advantage of movements in different economic zones.
Exotic Currency Pairs
Overview
Exotic currency pairs feature one major currency and one currency from an emerging or smaller economy. These pairs are less liquid, have wider spreads, and tend to be more volatile than major and minor pairs. However, they can offer substantial price movements and opportunities for profit.
Why consider exotic pairs? They provide unique trading opportunities and can react to different economic and political conditions compared to more traditional pairs.

Examples of Exotic Currency Pairs
Here are some examples of exotic currency pairs:
- USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira): Represents the US dollar against the Turkish lira.
- USD/SEK (US Dollar/Swedish Krona): Compares the dollar to the Swedish krona.
- USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South African Rand): Shows the value of the dollar relative to the South African rand.
- EUR/TRY (Euro/Turkish Lira): Reflects the euro’s value against the Turkish lira.
- GBP/SGD (British Pound/Singapore Dollar): Compares the pound to the Singapore dollar.
USD/TRY: Reflecting Emerging Markets
The USD/TRY pair shows the economic dynamics between the US and Turkey. It’s influenced by Turkish economic data, political events, and market sentiment. Due to its volatility, it offers significant trading opportunities but also higher risk.
Personal Experience: Trading USD/TRY
I recall trading USD/TRY during a period of political instability in Turkey. The lira was highly volatile, and by closely following news and market sentiment, I was able to take advantage of the rapid price movements. This experience emphasized the need for thorough research and readiness for sudden market changes.
The USD/SEK pair combines the US dollar and the Swedish krona, highlighting the economic relationship between the US and Sweden. Economic indicators and monetary policies in Sweden influence this pair. Traders use it to gain exposure to the Scandinavian market and diversify their trading strategies.
Factors Influencing Currency Pairs
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators are crucial in determining the value of currency pairs. Key indicators include Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation, employment figures, and trade balances. These indicators provide insight into a country’s economic health and can significantly impact currency values.
Table: Key Economic Indicators
| Indicator | Description | Impact on Currency Pairs |
|---|---|---|
| GDP | Measures economic performance | Strong GDP growth can strengthen a currency |
| Inflation | Measures the rate of price increases | High inflation can weaken a currency |
| Employment | Measures job creation and unemployment rates | Low unemployment can strengthen a currency |
| Trade Balance | Measures the difference between exports and imports | Trade surplus can strengthen a currency |
Central Bank Policies
Central bank policies, including interest rate decisions, quantitative easing, and forward guidance, play a significant role in currency valuation. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency, while lower rates can weaken it.
Anecdote: Central Bank Influence
I remember when the Federal Reserve announced a series of interest rate hikes. The immediate reaction was a significant appreciation of the US dollar against other currencies. Traders who anticipated this move were able to profit from the currency’s strengthening.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events such as political instability, elections, wars, and trade disputes can have profound effects on currency values. These events introduce uncertainty and volatility, leading to rapid changes in currency prices.
Case Study: Geopolitical Impact
During the Brexit referendum, the GBP/USD pair saw dramatic volatility. Traders who closely followed the news and political developments were able to make significant gains by predicting the market’s reaction to the referendum’s outcome.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment and trader psychology also influence currency movements. Positive sentiment can lead to currency appreciation, while negative sentiment can cause depreciation. Sentiment analysis helps traders gauge the overall mood of the market and make more informed decisions.
Personal Insight: Trading Strategies
Combining technical and fundamental analysis has been key to my trading success. By analyzing price charts and staying informed about economic and political developments, I’ve been able to make more informed trading decisions and improve my overall performance.
How to Trade Currency Pairs
Understanding Bid and Ask Prices
In forex trading, the bid price is the amount at which the market will buy the base currency, while the ask price is the amount at which the market will sell it. The difference between these two prices is known as the spread.
Table: Bid and Ask Prices
| Currency Pair | Bid Price | Ask Price | Spread |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 1.1000 | 1.1002 | 2 pips |
| USD/JPY | 110.50 | 110.52 | 2 pips |
| GBP/USD | 1.3000 | 1.3003 | 3 pips |
The spread represents the transaction cost for trading the pair. In more liquid markets, spreads tend to be narrower, while in less liquid markets, they can be wider.
Using Leverage
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. While it can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. It’s crucial to use leverage wisely and implement strong risk management strategies.
Personal Experience: Leveraged Trading
When I first began using leverage, I underestimated its risk. After a few significant losses, I learned to approach leveraged trading with caution. Implementing stricter risk management strategies became essential, and I realized how crucial it is to fully understand leverage’s impact on trading outcomes.
Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Technical Analysis: Focuses on studying historical price data and chart patterns. Tools like moving averages, the Relative Strength Index (RSI), and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) help traders identify trends and potential entry and exit points.
Fundamental Analysis: Involves evaluating economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical events to predict currency movements. By understanding the underlying factors that influence currency values, traders can make informed decisions based on economic data and market news.
Table: Technical vs. Fundamental Analysis
| Analysis Type | Focus | Tools and Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Analysis | Historical price data and chart patterns | Moving averages, RSI, MACD |
| Fundamental Analysis | Economic data and news events | GDP reports, interest rate decisions, political events |
Personal Insight: Trading Strategies
Throughout my trading career, I’ve found that combining technical and fundamental analysis provides a more comprehensive approach. By analyzing price charts and staying updated on economic and political developments, I’ve been able to make more informed decisions and enhance my trading performance.
FAQs
Currency pairs in forex trading represent the value of one currency relative to another. Each pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, EUR is the base currency and USD is the quote currency. This pair shows how many US dollars are needed to purchase one euro.
Currency pairs work by showing how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency. When traders buy a currency pair, they are buying the base currency and selling the quote currency. Conversely, selling a currency pair means selling the base currency and buying the quote currency.
Currency pairs are quoted in terms of how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. For example, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.1000, it means 1 euro is equivalent to 1.1000 US dollars.
Major currency pairs are the most traded pairs in the forex market and always include the US dollar (USD) on one side. Examples include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD. These pairs are known for their high liquidity, narrow spreads, and lower volatility.
Minor currency pairs, also known as cross-currency pairs, do not involve the US dollar. They include combinations of major currencies such as EUR/GBP or GBP/JPY. These pairs are less liquid than major pairs but still offer significant trading opportunities.
Exotic currency pairs consist of one major currency and one currency from an emerging or smaller economy. Examples include USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira) and USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South African Rand). Exotic pairs are known for their higher volatility and wider spreads compared to major and minor pairs.
Currency pair values are influenced by various factors including economic indicators (like GDP and inflation), central bank policies (interest rates and monetary policy), geopolitical events (political stability and trade disputes), and market sentiment (trader psychology and market trends).
The bid price is the price at which the market is willing to buy the base currency, while the ask price is the price at which the market is willing to sell the base currency. The difference between the bid and ask price is known as the spread.
Effective analysis of currency pairs involves both technical and fundamental approaches. Technical analysis uses historical price data and chart patterns to predict future movements, while fundamental analysis evaluates economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical events to understand underlying value.
Conclusion
Understanding currency pairs is fundamental to navigating the forex market. Whether you’re trading major, minor, or exotic pairs, grasping the nuances of each type and the factors that influence them is essential. By combining technical and fundamental analysis with effective risk management, traders can better position themselves for success.
Remember, mastering currency pairs will not only enhance your trading skills but also open up a world of opportunities in the dynamic forex market.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!