Types of Forex Orders (Market, Limit, Stop-Loss)
In the dynamic world of Forex trading, understanding the different types of Forex orders is crucial for effective and strategic trading. Forex orders are the specific instructions that traders provide to their brokers, dictating how and when to enter or exit trades in the Forex market. Each type of order plays a unique role in a trader’s strategy, and knowing when and how to use each one can make the difference between success and failure in trading.
The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, making it the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. With such a vast market, it’s essential for traders to not only understand market trends but also the mechanics of executing trades efficiently. This article delves deep into the various types of Forex orders, offering insights into their uses, benefits, and potential risks, all while providing a foundation for both novice and experienced traders to refine their trading strategies.
Contents
- What Are Forex Orders?
- Market Orders: Executing Trades Instantly
- Limit Orders: Controlling Your Entry and Exit Prices
- Stop Orders: Triggering Trades Based on Market Movements
- Stop Loss Orders: Safeguarding Your Trades
- Trailing Stop Orders: Protecting Profits
- Pending Orders: Planning Your Trades in Advance
- The Role of Technology in Forex Orders
- Common Mistakes to Avoid with Forex Orders
- Advanced Order Types and Strategies
- Forex Orders in Practice: A Case Study
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What Are Forex Orders?
At its core, a Forex order is an instruction to your broker to execute a trade on your behalf. Whether you’re buying or selling currency pairs, the type of order you choose determines the conditions under which the trade is executed. Forex orders allow traders to automate their trading strategies, ensuring that trades are executed at optimal prices and according to predefined rules.
Forex orders can be categorized into two main types: market orders and pending orders. Each category encompasses several specific order types, each with its own purpose and application in trading. Understanding these orders and how they function in different market conditions is essential for developing a robust trading plan.
Market Orders: Executing Trades Instantly
A market order is the simplest and most commonly used type of Forex order. It is an instruction to buy or sell a currency pair immediately at the best available price. When you place a market order, you are essentially telling your broker that you want to enter or exit the market at the current price without delay. This immediacy makes market orders ideal for traders who need to act quickly to capitalize on market opportunities.
How Market Orders Work
When a market order is placed, the broker executes the trade at the current market price. The price at which the order is filled may differ slightly from the price displayed when the order was placed, especially in fast-moving markets. This difference, known as slippage, occurs because the Forex market is highly volatile, and prices can change in milliseconds.
For example, if you want to buy the EUR/USD currency pair and the current price is 1.2100, placing a market order will execute the trade as close to this price as possible. However, in a highly volatile market, the actual execution price might be slightly higher or lower.
Advantages and Risks of Market Orders
The primary advantage of a market order is its speed. Market orders are executed almost instantaneously, allowing traders to take advantage of short-term market movements. This is particularly beneficial for day traders and scalpers who rely on quick executions to profit from small price fluctuations.
However, the main risk associated with market orders is slippage. In highly volatile markets, the price at which your order is executed may differ significantly from the expected price, potentially leading to unexpected losses. Therefore, while market orders offer speed, they come with the trade-off of less control over the execution price.
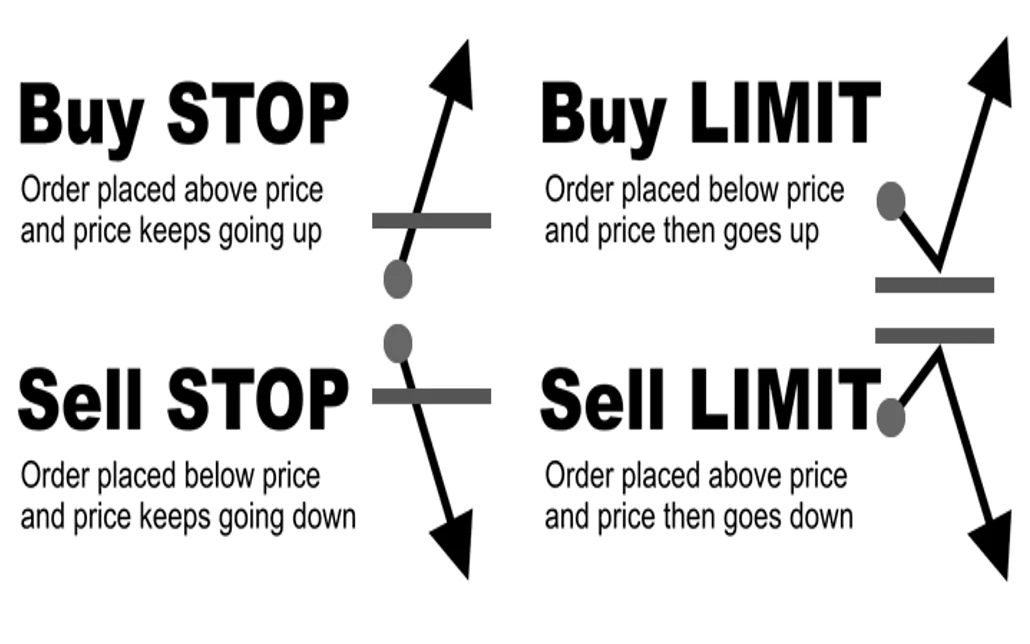
Limit Orders: Controlling Your Entry and Exit Prices
A limit order allows traders to specify the price at which they want to enter or exit a trade. Unlike market orders, which are executed at the best available price, limit orders are only executed at the specified price or better. This gives traders more control over their trades, allowing them to set precise entry and exit points based on their analysis of the market.
Buy Limit Orders
A buy limit order is placed below the current market price. It is used when a trader believes that the price of a currency pair will fall to a certain level before reversing and moving higher. The order is only executed if the market reaches or goes below the specified price, ensuring that the trader buys at a favorable price.
For instance, if the EUR/USD is currently trading at 1.2150, and you believe that the price will drop to 1.2100 before rising, you can place a buy limit order at 1.2100. The order will only be executed if the market price falls to or below 1.2100.
Sell Limit Orders
Conversely, a sell limit order is placed above the current market price. This type of order is used when a trader expects the price of a currency pair to rise to a certain level before reversing and moving lower. The order is executed only if the market price reaches or exceeds the specified level, allowing the trader to sell at a higher price.
For example, if GBP/USD is trading at 1.3800, and you anticipate that the price will rise to 1.3850 before dropping, you can place a sell limit order at 1.3850. The trade will be executed if the market reaches this price, ensuring a profitable sell.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Limit Orders
The main benefit of limit orders is the control they offer. Traders can set specific entry and exit points, ensuring that they only buy or sell at prices they consider favorable. This is particularly useful in markets where prices can be unpredictable, as it helps traders avoid the emotional decision-making that can lead to poor trading outcomes.
However, the drawback of limit orders is that they may not be executed if the market does not reach the specified price. In such cases, a trading opportunity might be missed. Moreover, in fast-moving markets, the price might touch the limit level briefly before moving away, resulting in a partial fill or no execution at all.
Stop Orders: Triggering Trades Based on Market Movements
A stop order, also known as a stop-loss order when used for risk management, is an instruction to buy or sell a currency pair once the market reaches a specified price, known as the stop price. Stop orders are typically used to limit losses or to enter the market in the direction of momentum once a specific price level is breached.
Buy Stop Orders
A buy stop order is placed above the current market price and is triggered when the price reaches or exceeds the stop level. This type of order is used when a trader believes that the market will continue to rise after breaking through a certain resistance level.
For example, if the USD/JPY pair is trading at 110.00, and you expect that a move above 110.50 will lead to further gains, you can place a buy stop order at 110.50. If the price reaches this level, the order will be executed, allowing you to enter the market at the best available price above 110.50.
Sell Stop Orders
Conversely, a sell stop order is placed below the current market price and is triggered when the price reaches or falls below the stop level. This type of order is used when a trader anticipates that the market will continue to decline after breaking through a certain support level.
For instance, if EUR/USD is trading at 1.2100, and you expect that a break below 1.2050 will lead to further losses, you can place a sell stop order at 1.2050. If the price reaches this level, the order will be executed, allowing you to enter a short position at the best available price below 1.2050.
Practical Uses of Stop Orders
Stop orders are essential tools for managing risk and executing momentum-based strategies. They are commonly used in breakout trading, where traders seek to capitalize on significant price movements that occur when the market breaks through key levels of support or resistance.
However, traders should be aware of the risks associated with stop orders, particularly in volatile markets. A sudden price spike can trigger stop orders, leading to trades being executed at unfavorable prices. Additionally, stop orders may be subject to slippage, especially during times of low liquidity or high volatility.
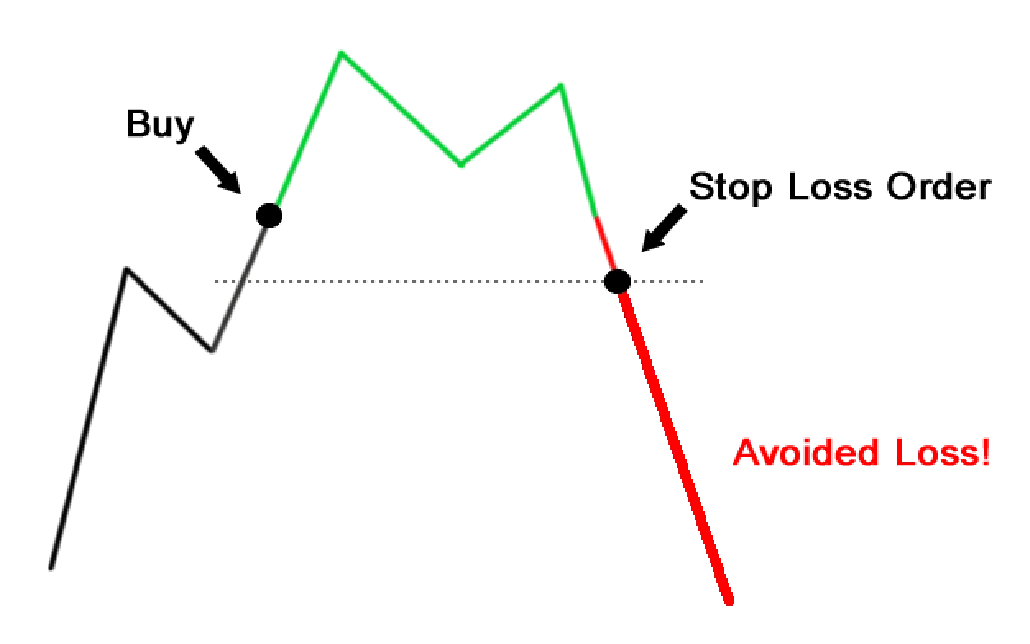
Stop Loss Orders: Safeguarding Your Trades
A stop loss order is a specific type of stop order designed to limit a trader’s loss on a position. It is an instruction to close a trade at a predetermined price if the market moves against the trader. Stop loss orders are crucial for risk management, as they help prevent large losses by automatically closing losing trades before they can cause significant damage to the trader’s account.
How Stop Loss Orders Work
When a stop loss order is placed, it is set at a price level below the entry price for a long position or above the entry price for a short position. If the market price reaches the stop level, the order is triggered, and the trade is closed at the best available price.
For example, if you have bought EUR/USD at 1.2200, you might place a stop loss order at 1.2170 to limit your potential loss to 30 pips. If the price drops to 1.2170, the stop loss order will be executed, and your position will be closed, capping your loss.
The Importance of Stop Loss Orders in Risk Management
Stop loss orders are vital tools for managing risk in Forex trading. They allow traders to set a maximum acceptable loss for each trade, ensuring that they do not lose more than they are willing to risk. This is particularly important in a market as volatile as Forex, where prices can move rapidly and unexpectedly.
However, while stop loss orders are effective at limiting losses, they are not foolproof. In highly volatile markets, the price can gap through the stop level, resulting in the trade being closed at a worse price than expected. This phenomenon, known as slippage, is a risk that traders must be aware of when using stop loss orders.
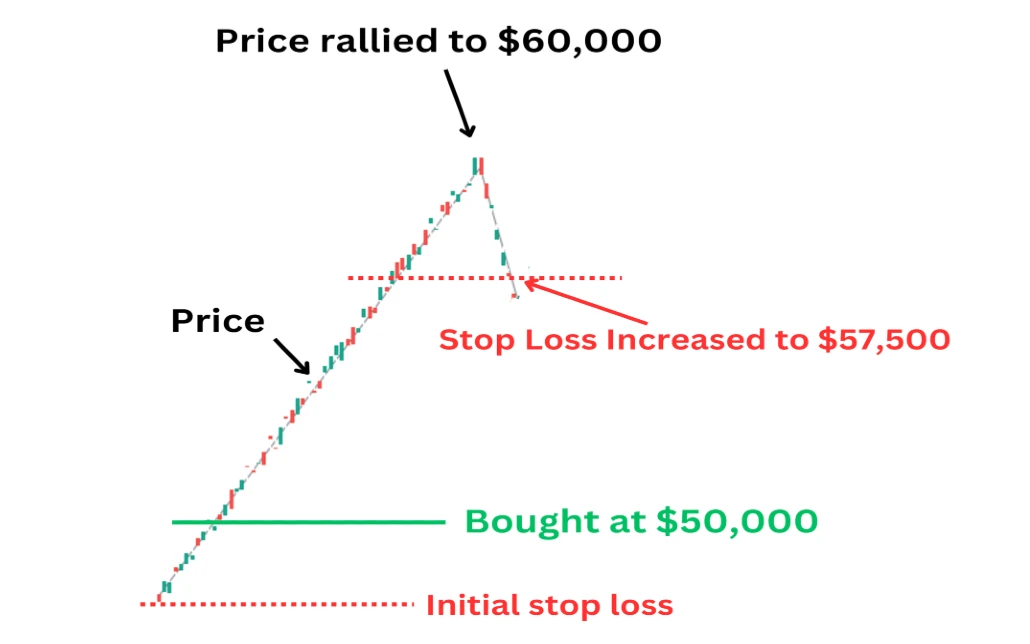
Trailing Stop Orders: Protecting Profits
A trailing stop order is a dynamic type of stop loss order that adjusts as the market price moves in your favor. Unlike a fixed stop loss, which remains at a set price level, a trailing stop moves with the market, locking in profits as the price moves in your favor. This allows traders to protect their gains while still giving the trade room to grow.
How Trailing Stop Orders Work
When you place a trailing stop order, you set a trailing amount, typically in pips, that determines how far the stop will trail behind the current market price. As the market price moves in your favor, the stop level moves with it, maintaining the specified distance. If the market price reverses, the stop level remains fixed at its last position, and if the price falls to this level, the trade is closed.
For example, if you buy USD/JPY at 110.00 and set a trailing stop of 20 pips, the initial stop loss will be set at 109.80. If the price rises to 110.40, the trailing stop will move up to 110.20, locking in 20 pips of profit. If the price then falls to 110.20, the trade will be closed, securing your profits.
Advantages of Using Trailing Stop Orders
The main advantage of trailing stop orders is that they allow traders to lock in profits while still giving the trade room to grow. As the market moves in your favor, the trailing stop moves with it, ensuring that your gains are protected. This is particularly useful in trending markets, where prices can continue to move in one direction for extended periods.
However, trailing stops can also be risky if set too tightly. If the trailing stop is too close to the current market price, it may be triggered by normal market fluctuations, causing the trade to be closed prematurely. Therefore, it is essential to set the trailing stop at a distance that allows for normal market movements while still protecting your profits.
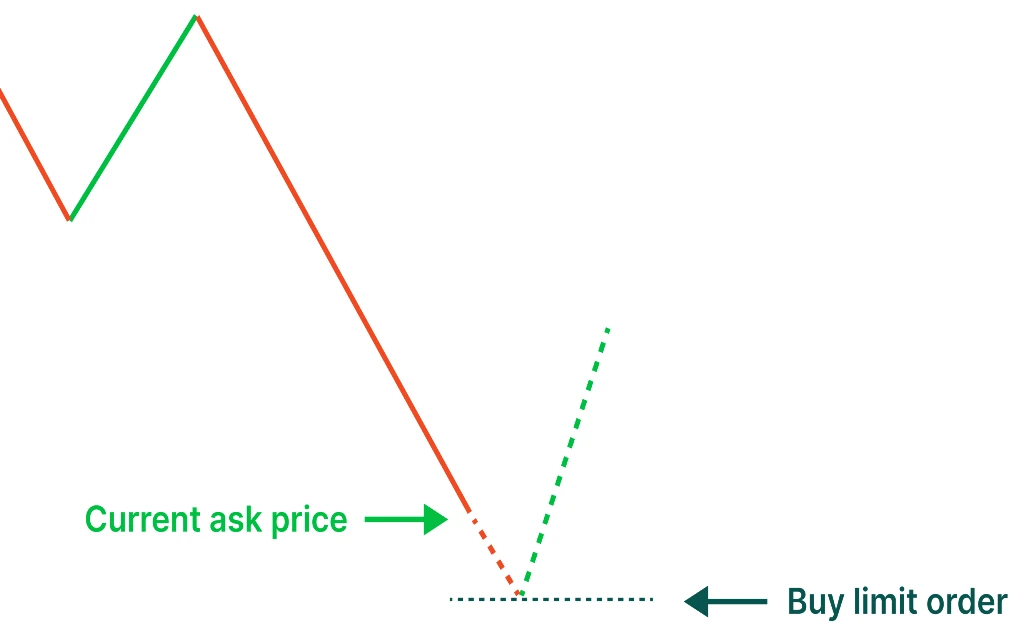
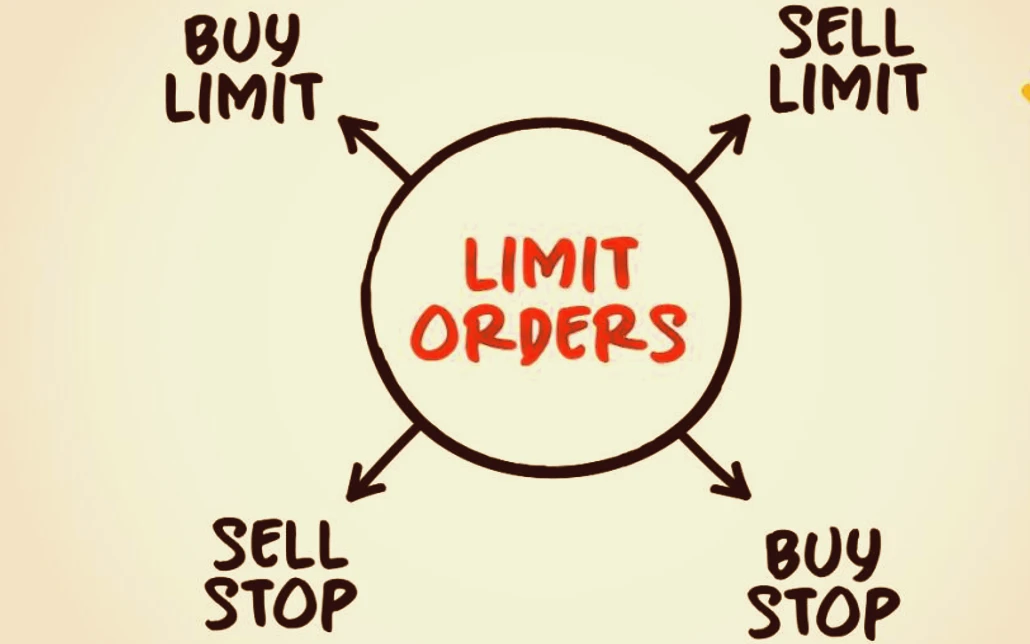
Pending Orders: Planning Your Trades in Advance
Pending orders are instructions to your broker to execute a trade at a specific price in the future. Unlike market orders, which are executed immediately, pending orders are placed in advance and are triggered only when the market reaches the specified price level. Pending orders are particularly useful for traders who want to enter the market at specific levels without having to monitor the market constantly.
Types of Pending Orders
There are four main types of pending orders in Forex trading: buy limit, sell limit, buy stop, and sell stop. Each type serves a different purpose, allowing traders to tailor their strategies to different market conditions.
- Buy Limit: An order to buy a currency pair at a price below the current market price.
- Sell Limit: An order to sell a currency pair at a price above the current market price.
- Buy Stop: An order to buy a currency pair at a price above the current market price.
- Sell Stop: An order to sell a currency pair at a price below the current market price.
Strategic Use of Pending Orders
Pending orders are essential tools for executing well-planned trading strategies. By placing pending orders at key levels, traders can ensure that they enter or exit the market at optimal prices, even if they are not actively monitoring the market.
For example, if you expect that the EUR/USD pair will break above a resistance level and continue rising, you can place a buy stop order just above the resistance level. If the price reaches this level, the order will be triggered, allowing you to enter the trade in the direction of the breakout.
Similarly, if you believe that the price will reverse after reaching a certain level, you can place a sell limit order at that level. This ensures that you sell at the highest possible price before the expected reversal.
The Role of Technology in Forex Orders
The rise of algorithmic trading has significantly impacted the way Forex orders are placed and executed. Algorithms, or trading bots, can execute orders at lightning speed, far surpassing human capabilities. This has led to the development of complex order types and strategies that were previously unimaginable.
Algorithmic trading allows for the automation of trading strategies, including the placement of market, limit, stop, and trailing stop orders. By programming specific conditions into the algorithm, traders can ensure that their orders are executed exactly as planned, without the need for manual intervention.
How Trading Platforms Influence Order Execution
The choice of trading platform plays a crucial role in how Forex orders are executed. Different platforms offer varying levels of functionality, speed, and reliability, all of which can impact the success of a trade. Advanced platforms provide features such as one-click trading, advanced charting tools, and the ability to place complex orders with ease.
For example, platforms like MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 offer extensive features for placing and managing orders, including built-in indicators and expert advisors (EAs) that can automate trading strategies. Choosing the right platform is essential for executing orders efficiently and effectively.
The Future of Forex Orders with AI and Machine Learning
The future of Forex orders is likely to be shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI)] and machine learning. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way trades are executed by analyzing vast amounts of market data and making real-time decisions based on patterns and trends.
AI and machine learning algorithms can optimize order placement by predicting market movements with greater accuracy. This could lead to the development of new order types that are more responsive to market conditions, further enhancing the precision and effectiveness of Forex trading strategies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Forex Orders
One of the most common mistakes traders make is over-leveraging, which involves using too much borrowed capital to increase the size of a trade. While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses, making it a double-edged sword. When combined with improper use of Forex orders, over-leveraging can lead to significant losses.
Effective risk management is essential for avoiding this pitfall. This includes using stop loss orders to limit potential losses and ensuring that the size of each trade is proportionate to your overall trading capital. By managing risk effectively, traders can avoid the devastating effects of over-leveraging.
Misunderstanding Order Types
Another common mistake is misunderstanding the various order types and how they function in different market conditions. For example, placing a market order in a highly volatile market without considering the potential for slippage can lead to unexpected losses. Similarly, using limit orders without understanding the risk of non-execution can result in missed opportunities.
To avoid these mistakes, traders should thoroughly educate themselves on the different types of orders and practice using them in a demo account before applying them in live trading.
Ignoring Market Conditions
Ignoring market conditions is another mistake that can lead to poor trading outcomes. Different market conditions, such as high volatility, low liquidity, or significant news events, can greatly affect how orders are executed. For example, during periods of low liquidity, there may be a greater risk of slippage, while high volatility can lead to rapid price movements that trigger stop orders unexpectedly.
Traders should always consider the current market environment when placing orders and adjust their strategies accordingly. This may involve widening stop levels during volatile periods or using pending orders to enter the market after significant news events.
Advanced Order Types and Strategies
Conditional orders are advanced order types that allow traders to set specific conditions that must be met before an order is executed. These orders are particularly useful for implementing complex trading strategies that involve multiple entry and exit points.
For example, a trader might set a conditional order to buy EUR/USD only if the price breaks above a certain level and the RSI (Relative Strength Index) exceeds a specified threshold. This allows for greater precision in executing trades based on technical indicators.
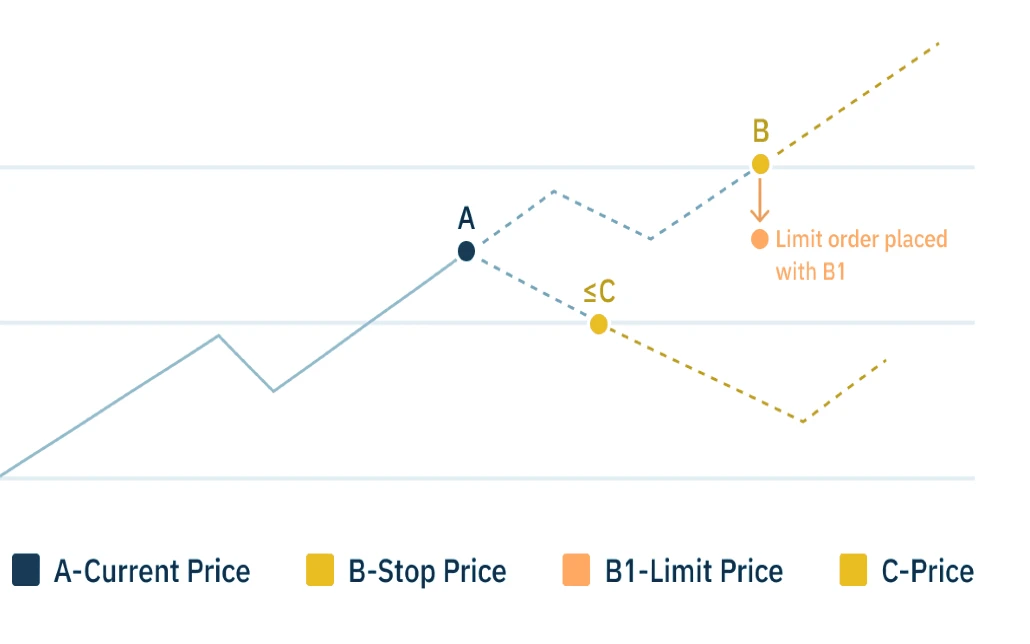
OCO (One Cancels the Other) Orders
An OCO (One Cancels the Other) order is a type of conditional order that consists of two linked orders. If one of the orders is executed, the other is automatically canceled. This type of order is often used to enter a trade if either a breakout or a breakdown occurs, allowing the trader to capitalize on the movement in either direction.
For example, a trader might place an OCO order with a buy stop above a resistance level and a sell stop below a support level. If the price breaks above the resistance level, the buy stop order is executed, and the sell stop order is canceled, ensuring that the trader enters the market in the direction of the breakout.
Combining Orders for Complex Strategies
Traders can combine different order types to create complex strategies that are tailored to specific market conditions. For example, a trader might use a combination of limit orders, stop orders, and trailing stops to execute a strategy that involves buying on dips, selling on rallies, and locking in profits as the market moves in their favor.
By combining orders, traders can create strategies that are both flexible and precise, allowing them to adapt to changing market conditions and maximize their potential for profit.
Forex Orders in Practice: A Case Study
To illustrate the practical application of Forex orders, let’s examine a case study involving a trader who successfully navigated a volatile market environment by strategically using different order types. This case study will provide insights into how orders can be used to manage risk, capitalize on opportunities, and achieve trading objectives.
Step-by-Step Analysis
The case study will follow the trader’s journey from market analysis to order placement and execution. We will explore how the trader identified key levels of support and resistance, placed pending orders to enter the market at optimal prices, and used stop loss and trailing stop orders to protect profits and limit losses.
Lessons Learned
The case study will conclude with a discussion of the lessons learned from the trader’s experience. This will include key takeaways on the importance of thorough market analysis, the effective use of different order types, and the value of discipline and patience in executing a successful trading strategy.
FAQs
A market order is executed immediately at the best available price, while a limit order is executed only if the market reaches a specified price. Market orders are used for quick entries or exits, whereas limit orders are used when a trader wants to buy or sell at a specific price.
A stop loss order automatically closes a trade when the market price reaches a predetermined level. It is used to limit potential losses on a trade. For example, if you buy a currency pair, you can set a stop loss order below the purchase price to sell automatically if the price drops to that level.
Slippage occurs when there is a difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which it is actually executed. This usually happens in fast-moving markets where prices change rapidly. Slippage can result in trades being executed at a less favorable price than intended.
Yes, traders often use multiple types of orders simultaneously to manage their trades more effectively. For example, you can place a limit order to enter a trade at a specific price, and at the same time, place a stop loss order to limit potential losses if the market moves against you.
A trailing stop order is a type of stop loss order that adjusts automatically as the market price moves in favor of the trade. It trails the market price by a set number of pips, helping to lock in profits while minimizing risk. If the market reverses direction by the specified amount, the order will be executed.
Yes, you can cancel a Forex order as long as it has not been executed. To cancel an order, you need to go to your trading platform and manually cancel the pending order. Once an order is executed, it cannot be cancelled, but you can place a new order to close the position.
To avoid common mistakes, ensure you understand the type of order you are placing, use stop loss orders to manage risk, and avoid overusing market orders, which can lead to slippage. Always place orders strategically based on thorough market analysis.
Advanced Forex orders, such as OCO (One-Cancels-the-Other) and GTC (Good Till Cancelled) orders, provide additional flexibility and control. These orders are typically used by experienced traders to fine-tune their trading strategies and manage risk more effectively.
It’s important to regularly review and adjust your Forex orders, especially in response to changing market conditions. Set alerts and monitor your trades to ensure that your orders are aligned with your trading strategy and risk management plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the different types of Forex orders is essential for successful trading. Each order type serves a specific purpose, from executing trades quickly with market orders to controlling entry and exit prices with limit orders, and managing risk with stop loss and trailing stop orders. By mastering these orders and knowing when and how to use them, traders can enhance their strategies, protect their capital, and increase their chances of success in the Forex market.
Final Thoughts on the Importance of Mastering Forex Orders
Forex trading is a complex and dynamic field that requires both knowledge and skill. Mastering the use of Forex orders is a critical component of becoming a successful trader. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding how to effectively use different order types will give you a significant advantage in the market. As the Forex market continues to evolve with advancements in technology and changes in market conditions, staying informed and adaptable will be key to maintaining success.
By continuing to educate yourself, practicing your strategies, and refining your use of Forex orders, you can navigate the challenges of the Forex market with confidence and achieve your trading goals.
Suggested Readings: Dive Deeper into Forex Trading
To enhance your understanding and mastery of Forex trading, consider exploring these in-depth resources:
Understanding the Forex Market Structure:
Gain a comprehensive understanding of how the Forex market operates, including the key players, trading hours, and major financial centers that drive global currency movements. This foundational knowledge is essential for any Forex trader.
Technical Analysis in Forex Trading:
Discover how to use technical indicators, chart patterns, and other analytical tools to forecast market movements. This guide is crucial for traders looking to develop a systematic approach to market analysis.
Fundamental Analysis for Forex Traders:
Learn how to interpret economic indicators, news events, and geopolitical developments to make informed trading decisions. Fundamental analysis helps you understand the broader forces that impact currency values.
Risk Management Strategies in Forex Trading:
Understand the importance of managing risk in Forex trading. This resource covers strategies like position sizing, diversification, and the use of stop-loss orders to protect your capital.
Psychology of Forex Trading:
Explore how emotions can impact your trading performance and learn techniques to develop a disciplined, objective trading mindset. Mastering the psychological aspects of trading is key to long-term success.
Algorithmic Trading in Forex:
Delve into the world of automated trading systems. Learn how algorithms work, the advantages they offer, and how you can start developing your own trading algorithms.
Introduction to Forex Trading for Beginners:
If you’re new to Forex trading, this beginner-friendly guide is the perfect starting point. It covers the basic concepts, common mistakes to avoid, and practical tips to help you get started with confidence.
The Role of Central Banks in Forex Markets:
Understand how central bank policies and actions influence currency markets. This analysis is crucial for anticipating market movements and identifying trading opportunities.
Forex Trading Strategies for Different Market Conditions:
Tailor your trading strategy to suit different market conditions, whether trending, ranging, or volatile. This guide helps you adapt your approach to maximize profitability in any market environment.
Leverage and Margin in Forex Trading:
Learn about the mechanics of leverage in Forex trading, the associated risks, and how to use it responsibly to amplify your trading results without exposing yourself to unnecessary risk.
These resources are designed to deepen your knowledge of Forex trading, providing you with the tools and insights needed to navigate the market effectively. Whether you are a novice or an experienced trader, these topics will help you refine your strategy and improve your trading performance.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!