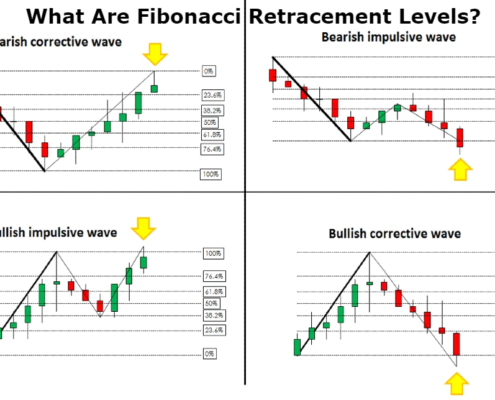
What Are Fibonacci Retracement Levels?
Fibonacci retracement levels are a fundamental tool in the arsenal of traders, serving as a vital resource for identifying potential support and resistance areas within the financial markets. These levels are derived from the Fibonacci sequence, a series of numbers that hold mathematical significance and are often observed in nature and art. Understanding Fibonacci retracement levels can greatly enhance a trader's ability to anticipate price movements, manage risk, and execute informed trades.
At their core, Fibonacci retracement levels are horizontal lines drawn on a price chart to indicate where the price of an asset may pause or reverse after a significant movement. The primary levels include 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%, each representing a percentage of the price movement between a peak and a trough. By applying these levels, traders can pinpoint potential reversal areas where price action may stall or change direction.
The Fibonacci sequence begins with the numbers 0 and 1, and each subsequent number is the sum of the two preceding ones. This unique series creates ratios that traders utilize to gauge price retracements. For example, if a stock rises from $50 to $100, and then retraces to the 61.8% level at $80.90, traders may see this as a potential buying opportunity, anticipating that the price will bounce back upwards.
One of the key aspects of Fibonacci retracement levels is their flexibility. Traders can apply them to any significant price movement, whether in stocks, currencies, commodities, or cryptocurrencies. This adaptability makes Fibonacci retracement levels a universal tool for technical analysis.
To effectively use Fibonacci retracement levels, traders must first identify two critical price points on a chart—typically a recent high and low. Once these points are established, the Fibonacci levels can be calculated and plotted, creating a visual representation of potential support and resistance zones. By analyzing price action around these levels, traders can make informed decisions about entry and exit points.
While Fibonacci retracement levels are valuable, they should not be solely relied upon for trading decisions. Traders often combine them with other technical indicators, such as moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), to enhance their analysis and confirm signals. This multi-faceted approach can lead to more accurate predictions and better trading outcomes.
Another important consideration is that Fibonacci retracement levels can provide insights into market psychology. Traders often react to these levels due to their popularity, leading to a self-fulfilling prophecy. For instance, if many traders are watching the 61.8% level and placing buy orders there, it may create upward pressure on the price, reinforcing the likelihood of a reversal at that point.
Despite their utility, Fibonacci retracement levels come with limitations. They do not guarantee price reversals; instead, they indicate potential areas of interest where reversals may occur. Additionally, the subjective nature of identifying significant high and low points can lead to discrepancies among traders. Different traders may draw Fibonacci levels based on varying interpretations of price action, leading to different conclusions about potential support and resistance zones.
In summary, Fibonacci retracement levels are an essential tool for traders seeking to enhance their technical analysis and trading strategies. By understanding the underlying mathematics of the Fibonacci sequence, calculating and plotting these levels, and integrating them with other technical indicators, traders can gain a more comprehensive view of market dynamics. As with any trading tool, experience and practice will refine a trader's ability to effectively utilize Fibonacci retracement levels, helping them navigate the complexities of the financial markets with greater confidence.
Whether you are a novice trader looking to expand your toolkit or a seasoned investor seeking to incorporate Fibonacci levels into your strategy, understanding these retracement levels can provide valuable insights and opportunities in your trading journey. As financial markets continue to evolve, mastering the art of technical analysis through tools like Fibonacci retracement levels can empower traders to make informed decisions and achieve their financial goals.
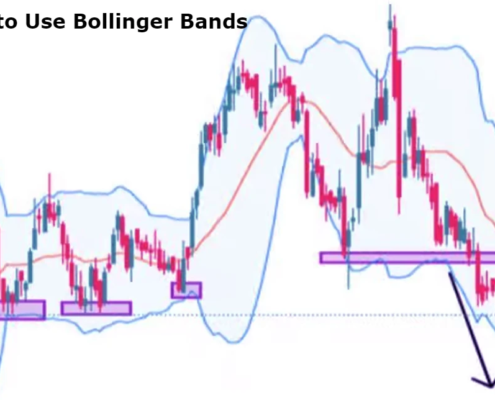
How to Use Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are a widely used technical analysis tool that helps traders assess market volatility and identify potential trading opportunities. Developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, this indicator consists of three lines: a simple moving average (SMA) at its center and two outer bands that represent standard deviations from this average. Understanding how to use Bollinger Bands effectively can significantly enhance your trading strategies and decision-making process.
At the heart of Bollinger Bands lies the concept of volatility. As market conditions change, the distance between the upper and lower bands will fluctuate. When the bands expand, it indicates increased volatility, while a contraction suggests a period of low volatility. This dynamic nature allows traders to gain insights into potential price movements and market behavior. By learning to interpret these signals, traders can identify trends, potential reversals, and the best entry and exit points for their trades.
One of the most significant advantages of Bollinger Bands is their ability to highlight overbought and oversold conditions. When prices approach the upper band, it often signals that the asset may be overbought, indicating a potential pullback or reversal is on the horizon. Conversely, prices nearing the lower band suggest oversold conditions, which can hint at a possible rebound. This characteristic makes Bollinger Bands a powerful tool for both trend-following strategies and reversal trading tactics.
Calculating Bollinger Bands is relatively straightforward, but it requires a good understanding of basic statistics. The middle band is typically a 20-period simple moving average, while the upper and lower bands are calculated by adding and subtracting two standard deviations from the SMA, respectively. This calculation provides a clear visual representation of the price range within which the asset is expected to trade. Traders often adjust the parameters based on their trading style and the asset's behavior, allowing for a customized approach to volatility analysis.
Interpreting Bollinger Bands involves recognizing price interactions with the bands and understanding their implications. For example, when a price consistently touches the upper band during an uptrend, it confirms the strength of the bullish movement. On the other hand, if prices frequently touch the lower band during a downtrend, it reinforces the bearish momentum. By combining Bollinger Bands with other technical indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), traders can enhance their analysis and improve decision-making.
In addition to trend-following and reversal strategies, Bollinger Bands can also be employed in a squeeze strategy. A squeeze occurs when the bands contract, signaling a period of low volatility that often precedes a significant price movement. Traders can prepare for potential breakouts by placing buy orders above the upper band and sell orders below the lower band, confirming these signals with volume spikes or other indicators.
While Bollinger Bands offer valuable insights, they are not without limitations. One common pitfall is overreliance on this indicator without considering other market factors. Traders should remain aware of the broader market context, including economic news and events that can impact price movements. Additionally, Bollinger Bands can generate false signals, especially in choppy market conditions. Therefore, incorporating other indicators and tools into your trading strategy is essential for a well-rounded approach.
In conclusion, mastering Bollinger Bands can significantly enhance your trading prowess by providing valuable insights into market volatility and price movements. By understanding their components, calculations, and interpretations, traders can make informed decisions that improve their chances of success. As with any trading strategy, practice and experience are crucial in developing your unique approach to using Bollinger Bands effectively. By integrating this powerful tool into your trading arsenal, you can gain a competitive edge in navigating the complexities of the financial markets.

Benefits of Using VPS for Forex Trading
In the fast-paced world of forex trading, where every millisecond can mean the difference between profit and loss, having a reliable and efficient trading environment is crucial. This is where a Virtual Private Server (VPS) comes into play. A forex VPS offers traders a dedicated and secure space to host their trading software, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing the risks associated with local technical issues.
One of the most significant benefits of using a VPS for forex trading is the enhanced speed of trade execution. When you host your trading software on a VPS located near your broker’s server, you drastically reduce latency. This proximity allows your trade orders to be processed more quickly, which is essential in a market that can change in an instant. For traders who utilize automated strategies, such as expert advisors (EAs), this speed is not just beneficial; it’s often critical to the success of their trading strategy.
Security is another paramount concern for traders, especially those dealing with sensitive financial information. A reputable VPS provider implements robust security protocols, including firewalls, antivirus software, and regular updates, ensuring that your trading environment is protected from potential threats. Additionally, many VPS services offer data encryption, safeguarding your login credentials and trading details from unauthorized access. This level of security allows traders to focus on their strategies without constantly worrying about cyber threats.
The uninterrupted trading experience provided by a VPS is another compelling reason to consider this solution. Unlike trading from a personal computer, where local issues such as power outages or internet disruptions can derail your trading activities, a VPS operates independently in a data center with redundant power and high-speed internet connections. This means you can access your trading platform 24/7, execute trades, and manage your portfolio from anywhere in the world without interruptions.
Moreover, using a VPS can be a cost-effective solution in the long run. While some traders may hesitate to invest in a VPS due to initial costs, the potential for increased profits through faster execution and reduced slippage can outweigh these expenses. Many VPS providers offer flexible pricing options, allowing traders to choose plans that best fit their budget and trading needs.
Flexibility and scalability are also significant advantages of utilizing a VPS for forex trading. Traders can customize their trading environment according to their preferences, install specific software, and run multiple instances of trading platforms without the limitations of local hardware. As traders' needs evolve, they can easily scale their VPS resources up or down, ensuring that they always have the performance necessary to execute their trading strategies effectively.
In summary, the benefits of using a VPS for forex trading are extensive. From faster execution speeds and enhanced security to an uninterrupted trading experience and cost-effectiveness, a VPS is an essential tool for traders looking to optimize their performance in the competitive forex market. By investing in a reliable VPS service, you can ensure that your trading platforms operate at their best, allowing you to capitalize on market opportunities and maximize your profit potential. With the ever-evolving nature of forex trading, leveraging advanced technology like a VPS will undoubtedly help you stay ahead of the curve and achieve your financial goals more effectively.
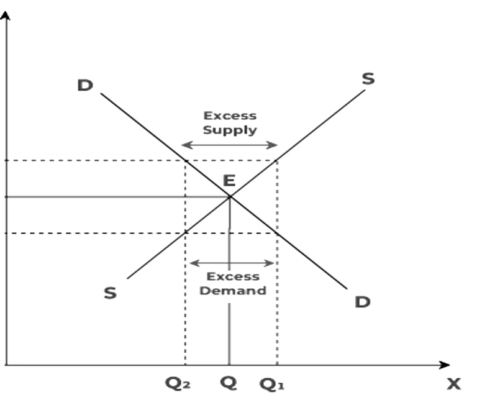
How Exchange Rates are Determined
Exchange rates represent the value of one currency in relation to another, directly affecting everything from the cost of imports to the profitability of exports. They are not static; they fluctuate based on a myriad of factors, including economic indicators, market sentiment, and geopolitical events.
At its core, an exchange rate indicates how much of one currency can be exchanged for another. For instance, if the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar (USD) and the euro (EUR) is 1.07, it means that one euro can be exchanged for $1.07. Such rates can significantly influence consumer purchasing power and the overall health of economies.
Exchange rates can be categorized into two main types: floating and fixed. A floating exchange rate fluctuates freely based on supply and demand dynamics in the foreign exchange market, reflecting the economic health and monetary policies of the respective countries. On the other hand, a fixed exchange rate is pegged to another currency or a basket of currencies, providing stability at the cost of flexibility.
One key aspect of understanding exchange rates is recognizing the various factors that influence them. Economic indicators such as interest rates, inflation, and unemployment rates are critical in shaping currency values. For instance, when a country's central bank raises interest rates, it typically leads to currency appreciation as higher rates attract foreign investment. Conversely, high inflation erodes purchasing power, often leading to depreciation of the currency.
Another vital element in the exchange rate equation is market sentiment and speculation. Traders in the foreign exchange market often buy and sell currencies based on expectations of future movements. For example, if investors believe that a country’s economy is set to improve, they may increase demand for its currency, driving up its value. This speculative activity can lead to rapid fluctuations in exchange rates, sometimes independent of economic fundamentals.
In addition to these factors, political stability plays a crucial role in determining exchange rates. Countries with stable governments and sound economic policies tend to attract foreign investment, which strengthens their currency. In contrast, political turmoil can lead to uncertainty and a decline in currency value as investors seek safer havens.
For businesses engaged in international trade, fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact profitability. A weakening currency can make exports cheaper and more competitive abroad, potentially boosting sales. However, it can also increase the cost of imports, leading to higher expenses for companies reliant on foreign goods. Understanding these dynamics is essential for developing effective pricing strategies and managing risks associated with currency fluctuations.
To mitigate the risks associated with exchange rate volatility, businesses often employ hedging strategies. Forward contracts, for instance, allow companies to lock in exchange rates for future transactions, providing certainty in budgeting and pricing. Currency options give businesses the right, but not the obligation, to exchange currencies at predetermined rates, offering flexibility alongside protection against adverse movements.
In conclusion, understanding how exchange rates are determined is vital for anyone navigating the complexities of international finance. From economic indicators to market sentiment, numerous factors influence currency values, making it essential for businesses and individuals alike to stay informed. Whether you are an investor, a traveler, or a business owner, grasping the intricacies of exchange rates can lead to more informed decisions and better financial outcomes. As global trade continues to evolve, being well-versed in how exchange rates operate will only grow in importance.
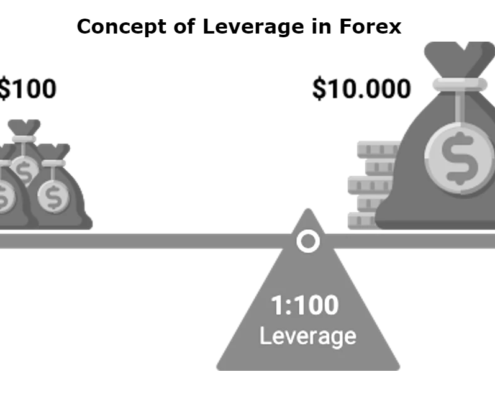
The Concept of Leverage in Forex
In the world of forex trading, leverage is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance your trading potential. Essentially, leverage allows traders to control larger positions in the market with a smaller amount of capital. This means that with a modest initial investment, you can take advantage of price movements in currency pairs, amplifying both potential profits and losses.
Leverage is expressed as a ratio, such as 100:1 or 50:1. For instance, with a leverage ratio of 100:1, you can control a position worth $100,000 with just $1,000 of your own money. This characteristic of forex trading is one of the main attractions for traders seeking to maximize their returns in a highly volatile market.
However, while the potential for greater profits is enticing, it’s crucial to understand that leverage also comes with substantial risks. The same leverage that can increase your gains can just as easily amplify your losses. If the market moves against your position, you could lose more than your initial investment, leading to a margin call from your broker. This occurs when your account equity falls below the required margin level, prompting you to deposit additional funds or close positions to avoid liquidation.
Understanding Margin and Leverage
To fully grasp leverage, it's important to also understand margin. Margin is the amount of capital required to open and maintain a leveraged position. When you enter a trade with leverage, your broker requires you to deposit a certain percentage of the total trade size as margin. This acts as a safety net for the broker, ensuring that you have enough capital to cover potential losses.
For example, if you want to trade a currency pair with a value of $50,000 at a leverage ratio of 100:1, you would need to deposit $500 as margin. This allows you to control a larger amount of currency while only risking a fraction of the total value. However, this also means that your potential for loss is tied to the entire value of the position, not just your initial margin deposit.
The Benefits of Using Leverage
Leverage can be an incredibly effective strategy for increasing your trading potential. One of the primary benefits of leverage is the ability to amplify your returns. In a market where currency values fluctuate rapidly, even small price movements can lead to significant profits when using leverage. For example, a 1% increase in a currency pair can yield a much larger return on investment when you are leveraged 100:1 compared to trading without leverage.
Additionally, leverage allows for greater flexibility in your trading strategy. With a smaller initial investment, you can diversify your portfolio by trading multiple currency pairs simultaneously. This diversification can help spread risk and increase your chances of capitalizing on favorable market conditions.
The Risks Associated with Leverage
Despite its benefits, trading with leverage carries considerable risks that every trader should be aware of. The primary risk is the potential for rapid losses. Since leverage magnifies both profits and losses, a small adverse movement in the market can quickly lead to significant financial consequences. Traders must be prepared for the possibility of losing more than their initial investment, which can lead to account depletion and margin calls.
Furthermore, the emotional aspect of trading with leverage cannot be overlooked. The prospect of large gains can lead to impulsive decision-making and over-leveraging, which increases exposure to risk. It’s essential for traders to maintain discipline and develop a solid risk management strategy to mitigate these dangers.
Conclusion: Navigating Leverage in Forex Trading
Leverage is a double-edged sword in forex trading; it can lead to impressive gains or devastating losses. Understanding how leverage works, the importance of margin, and the associated risks is vital for anyone looking to trade in the forex market. By employing effective risk management strategies and maintaining a disciplined approach, traders can harness the power of leverage to enhance their trading performance.
As you embark on your forex trading journey, remember to educate yourself about the intricacies of leverage and stay informed about market conditions. With careful planning and a strategic mindset, you can navigate the complexities of leverage and make informed decisions that align with your trading goals.

What is a Pip in Forex Trading?
In the world of forex trading, understanding the concept of a "pip" is fundamental for anyone looking to navigate the markets effectively. A pip, or "percentage in point," represents the smallest price movement that a currency pair can make based on market convention. For most currency pairs, this is typically the last decimal place in a price quote, while for Japanese yen pairs, it is the second decimal place. For example, if the EUR/USD moves from 1.1050 to 1.1051, that change of 0.0001 represents one pip. This seemingly simple concept carries significant weight in the forex market, impacting everything from profit calculations to risk management strategies.
The importance of pips extends beyond mere price movement; they serve as a universal language for traders. By standardizing the way price changes are communicated, traders can easily discuss market movements and share insights without confusion. Understanding pips allows traders to quantify gains and losses precisely, which is crucial for evaluating performance and refining trading strategies.
Moreover, pips are vital for effective risk management. Knowing the value of each pip in relation to your account's base currency enables you to set more accurate stop-loss orders and take-profit targets. This level of precision helps ensure that your trading capital is protected while still allowing for the potential to capitalize on favorable market movements.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the mechanics of pips, explore how to calculate pip values for different currency pairs, and discuss the role of pips in various trading strategies. We will also cover related concepts like pipettes and lots, providing a well-rounded understanding of the forex landscape. Whether you're a beginner just starting out or a seasoned trader looking to refine your knowledge, this guide will equip you with the information you need to navigate the forex markets confidently.
By mastering the concept of pips, you’ll not only enhance your trading acumen but also increase your chances of success in the fast-paced world of forex trading. Join us as we unravel the intricacies of pips and their impact on your trading journey.

Types of Forex Orders (Market, Limit, Stop-Loss)
When it comes to Forex trading, understanding the different types of orders is essential to executing a successful trading strategy. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned trader, knowing when and how to use market orders, limit orders, stop-loss orders, and more can be the difference between consistent profits and substantial losses.
In the fast-paced world of Forex, where prices can change in a fraction of a second, the ability to enter and exit trades at the right time and price is crucial. Forex orders are the tools that allow you to do just that, giving you control over your trading activities and helping you manage risk effectively.
Market Orders: Immediate Execution
A market order is the most straightforward type of Forex order. When you place a market order, you're instructing your broker to buy or sell a currency pair immediately at the best available price. This type of order is ideal when you want to enter or exit the market quickly without concern for minor fluctuations in price.
For example, if the EUR/USD pair is trading at 1.2140/1.2142, and you want to buy immediately, you would place a buy market order, which would execute at the ask price of 1.2142. The main advantage of market orders is their speed; they are executed almost instantly. However, this speed comes with a trade-off: you have no control over the exact price at which the order will be filled. In volatile markets, this can lead to slippage, where the final execution price differs from the expected price.
Limit Orders: Precision in Entry and Exit
Limit orders offer traders more control over the price at which a trade is executed. A limit order is placed to buy or sell a currency pair at a specific price or better. There are two main types of limit orders: buy limit orders and sell limit orders.
Buy Limit Order: This order is placed below the current market price. It instructs the broker to execute the order only if the price drops to the specified level. For instance, if EUR/USD is trading at 1.2050, and you believe the price will dip to 1.2000 before rising again, you would place a buy limit order at 1.2000.
Sell Limit Order: Conversely, a sell limit order is placed above the current market price. It will be executed only if the price rises to the specified level. If EUR/USD is at 1.2050 and you want to sell if the price reaches 1.2070, you would place a sell limit order at 1.2070.
Limit orders are particularly useful when you have a specific entry or exit price in mind and are not in a rush to execute the trade. The main advantage is the precision they offer; you know exactly the price at which your trade will be executed, or better. However, the downside is that the market might never reach your specified price, leaving the order unfilled.
Stop-Loss Orders: Protecting Your Capital
A stop-loss order is a crucial tool for risk management in Forex trading. It is designed to automatically close a position when the market moves against you by a specified amount, limiting your potential loss. Stop-loss orders can be used to protect both long and short positions.
Long Position (Buy): If you've bought a currency pair, you can place a sell stop-loss order below the purchase price. For example, if you bought EUR/USD at 1.2230, you might set a stop-loss order at 1.2200. If the price drops to 1.2200, the stop-loss order will be triggered, and your position will be closed, limiting your loss to 30 pips.
Short Position (Sell): Conversely, if you've sold a currency pair, you can place a buy stop-loss order above the sale price to protect against a rising market. If you shorted GBP/USD at 1.5050, you might set a stop-loss order at 1.5080. If the price rises to 1.5080, the order will close your position, limiting your loss.
The primary benefit of stop-loss orders is that they help traders avoid significant losses, especially in volatile markets. They allow you to set a maximum acceptable loss, giving you peace of mind and enabling you to focus on other trading opportunities without constantly monitoring the market. However, it’s important to note that in highly volatile markets, stop-loss orders may experience slippage, meaning the execution price could differ slightly from the stop price.
Trailing Stop Orders: Securing Profits While Reducing Risk
A trailing stop order is an advanced type of stop-loss order that adjusts as the market price moves in your favor. Instead of setting a fixed stop price, a trailing stop follows the market price by a set number of pips. As the market price increases, the trailing stop price moves up, helping you secure profits. If the market price reverses by the specified number of pips, the trailing stop is triggered, and the position is closed.
For example, suppose you go long on USD/JPY at 110.00 with a trailing stop set 20 pips below the market price. If the price rises to 110.40, the trailing stop would move up to 110.20. If the price then drops to 110.20, the trailing stop order would be triggered, locking in a 20-pip profit.
Trailing stops are particularly useful in trending markets where you expect the price to move significantly in one direction but want to protect against potential reversals. They allow you to ride the trend while reducing the risk of losing the profits you’ve gained.
Choosing the Right Forex Order
The type of Forex order you choose depends on your trading strategy, market conditions, and risk tolerance. Market orders are best for quick execution, while limit orders provide more control over the price at which trades are executed. Stop-loss and trailing stop orders are essential for managing risk and securing profits.
By understanding and effectively using these different types of orders, you can enhance your trading strategy, protect your capital, and improve your chances of success in the Forex market. Whether you’re executing a quick market order or setting up a strategic limit or stop-loss order, each type serves a specific purpose in your trading arsenal, helping you navigate the complexities of the Forex market with greater confidence.

Relative Strength Index (RSI) Indicator
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is one of the most widely used technical analysis indicators. Developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr. in 1978, the RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and magnitude of a security's recent price movements.…

Best Books for Forex Traders
Navigating the forex market can be a challenge, whether you're just starting out or have years of experience under your belt. With the right knowledge, though, you can turn this challenge into an opportunity for success. That’s why we’ve curated a list of the top 10 best books for forex traders. These books are packed with practical advice, proven strategies, and expert insights designed to help you understand the intricacies of the forex market.
Among these must-reads is "Currency Trading for Dummies", a perfect starting point for beginners that breaks down complex concepts into simple, understandable terms. For those looking to dive deeper into technical analysis, "Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets" by John J. Murphy is an essential guide that covers everything from basic chart patterns to advanced indicators. Meanwhile, "Trading in the Zone" by Mark Douglas delves into the psychological aspects of trading, helping you develop the mindset needed for consistent success.
Whether you're aiming to improve your trading strategies, manage risks more effectively, or gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics, these books offer invaluable resources that can significantly enhance your trading journey. Don’t miss out on these essential reads that could be the key to your next trading breakthrough.

Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading has transformed the financial markets, offering a cutting-edge approach to executing trades with precision, speed, and efficiency. At its core, algorithmic trading involves using computer programs to follow a predefined set of rules—based on timing, price, volume, or complex mathematical models—to place trades. This method significantly reduces the impact of human emotions on trading decisions, leading to a more systematic approach.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the evolution of algorithmic trading, from its early days in the 1970s to its current dominance in the financial markets. We explore various trading strategies such as trend-following, arbitrage, and high-frequency trading, and discuss the critical role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the future of trading.
The guide also covers the challenges and ethical considerations of algorithmic trading, emphasizing the importance of human oversight and regulatory compliance. Whether you're a seasoned trader or a beginner, this resource provides valuable insights and practical advice to help you navigate the complex world of algorithmic trading, optimize your strategies, and stay ahead of the curve.

