Forex Trading Strategies: Mastering the Art of Currency Trading
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, involves buying and selling currencies to make a profit. It’s a complex, dynamic market with a daily turnover exceeding $6 trillion, making it the largest financial market globally. To navigate this vast landscape, traders employ various strategies, each with its own set of rules, methodologies, and goals. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the most effective forex trading strategies, providing detailed insights and actionable tips for traders of all levels.
Understanding these strategies is crucial for both novice and experienced traders. While some strategies focus on short-term gains, others emphasize long-term trends. By exploring a range of strategies, traders can find the one that best suits their trading style, risk tolerance, and financial goals. This guide aims to equip traders with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions and enhance their trading performance.
Contents [hide]
Understanding Forex Trading
Before diving into specific strategies, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental concepts of forex trading. Forex trading involves the exchange of one currency for another, with the aim of capitalizing on fluctuations in exchange rates. Traders use various tools and techniques to predict these fluctuations and execute trades accordingly.
Understanding the forex market requires knowledge of how currency pairs are traded, the factors that influence exchange rates, and the role of market participants. The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, providing continuous opportunities for traders. Additionally, it is decentralized, meaning that trading occurs directly between parties, rather than through a centralized exchange.
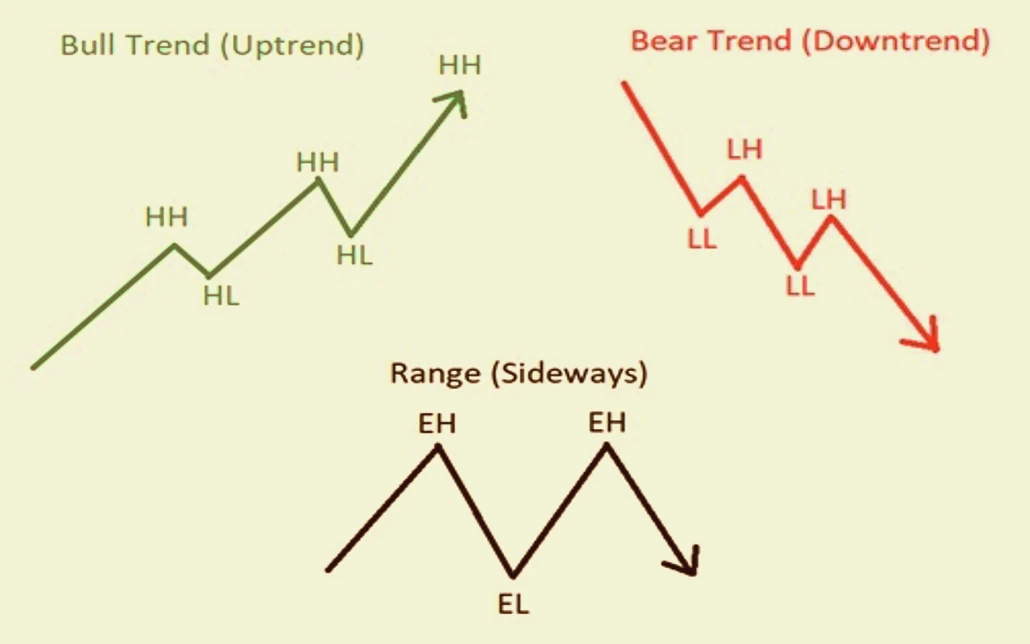
The Forex Market Structure
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with major trading sessions in London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney. The market is decentralized, meaning trades occur over-the-counter (OTC) rather than on a centralized exchange. This structure allows for continuous trading and provides ample opportunities for traders to enter and exit positions based on market movements and their trading strategies.
The decentralized nature of the forex market means that there is no single exchange or central clearinghouse. Instead, trading occurs directly between participants, facilitated by a network of banks, brokers, and other financial institutions. This setup provides liquidity and flexibility but also requires traders to stay informed about global economic and political events that can impact currency prices.
Key Participants in the Forex Market
The forex market is made up of various participants, each with their own motivations and goals:
- Central Banks: Influence currency prices through monetary policy and interventions.
- Commercial Banks: Facilitate transactions for clients and themselves.
- Hedge Funds: Engage in speculative trading to generate profits.
- Corporations: Conduct currency transactions for international trade.
- Retail Traders: Individual investors trading for personal profit.
Each of these participants plays a distinct role in the forex market, contributing to its liquidity and volatility. Central banks, for example, can significantly influence currency prices through their monetary policy decisions. Meanwhile, commercial banks and hedge funds engage in large-volume trades that can create substantial price movements. Understanding the actions and strategies of these participants can provide valuable insights for retail traders.
Understanding Currency Pairs
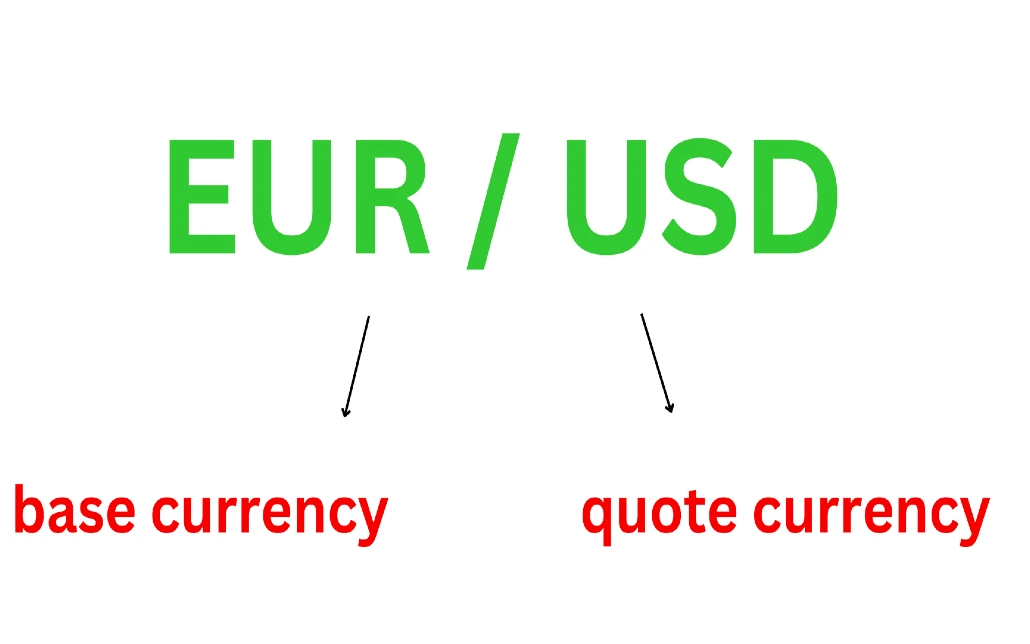
Currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY. The first currency is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency. The exchange rate indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency. This system allows traders to speculate on the relative strength of one currency against another, offering numerous trading opportunities.
For example, if a trader believes that the Euro will strengthen against the US Dollar, they might buy the EUR/USD pair. Conversely, if they believe the Euro will weaken, they might sell the pair. Understanding currency pairs and how they work is fundamental to forex trading, as it forms the basis for all transactions in the market.
Types of Forex Trading
Forex trading can be conducted in several different ways, each with its own characteristics and benefits:
- Spot Market: Immediate delivery of currencies.
- Forward Market: Contracts to buy/sell currencies at a future date.
- Futures Market: Standardized contracts traded on exchanges.
The spot market is the most common form of forex trading, involving the direct exchange of currencies at current market prices. The forward and futures markets, on the other hand, involve agreements to exchange currencies at a future date, often used for hedging or speculative purposes. Each type of trading offers different opportunities and risks, and traders must choose the approach that best aligns with their objectives and risk tolerance.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a country’s economic indicators, political stability, and overall economic health to predict currency movements. Traders analyze various factors, including interest rates, employment data, and geopolitical events.
Fundamental analysis helps traders understand the underlying forces that drive currency prices. By examining economic indicators and events, traders can make informed predictions about future price movements. This approach requires staying updated with global news and understanding how different factors interact to influence the forex market.
Key Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into a country’s economic health and can significantly impact currency prices:
- Interest Rates: Central banks adjust interest rates to control inflation and stabilize the economy.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total economic output of a country.
- Employment Data: Reflects the health of the labor market.
- Inflation Rates: Indicates the rate at which prices are rising.
- Trade Balance: Difference between a country’s exports and imports.
Each of these indicators offers a glimpse into different aspects of an economy. For instance, rising interest rates typically attract foreign investment, boosting the currency’s value. Conversely, high inflation may weaken a currency as it erodes purchasing power. Understanding these indicators and their implications is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
Analyzing Central Bank Policies
Central banks play a crucial role in the forex market. Traders closely monitor policy announcements and minutes from central bank meetings to gauge future monetary policy directions. Changes in interest rates, quantitative easing measures, and economic outlooks can significantly impact currency values.
For example, if a central bank signals an interest rate hike, the currency typically appreciates due to the anticipated increase in returns for investors. On the other hand, dovish policies or quantitative easing can lead to currency depreciation. Traders need to stay informed about central bank actions and their potential impact on the market to make well-timed trades.
Geopolitical Events and Forex
Political stability and geopolitical events can cause sharp movements in currency prices. Elections, policy changes, trade agreements, and conflicts are all factors that traders consider. Understanding the potential impact of these events helps traders anticipate market reactions.
For instance, a major political event such as Brexit can create significant volatility in the forex market. Traders need to be aware of such events and their potential implications on currency pairs. Geopolitical analysis involves understanding both the immediate and long-term effects of political decisions and events on the forex market.
Using Economic Calendars
Economic calendars provide a schedule of upcoming economic events and data releases. Traders use these calendars to plan their trades around significant announcements, such as non-farm payroll reports, central bank meetings, and GDP releases.
By staying informed about scheduled events, traders can prepare for potential market volatility. For example, a trader might choose to close positions ahead of a major economic announcement to avoid unexpected market movements. Economic calendars are essential tools for traders to manage their strategies and risk exposure effectively.
Technical Analysis in Forex Trading
Technical analysis involves studying historical price charts and using various indicators to predict future price movements. This approach is based on the belief that historical price action tends to repeat itself due to market psychology.
Technical analysis helps traders identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential reversal points. By analyzing past price movements, traders can develop strategies based on patterns and indicators. This method requires a solid understanding of different chart types and technical indicators.
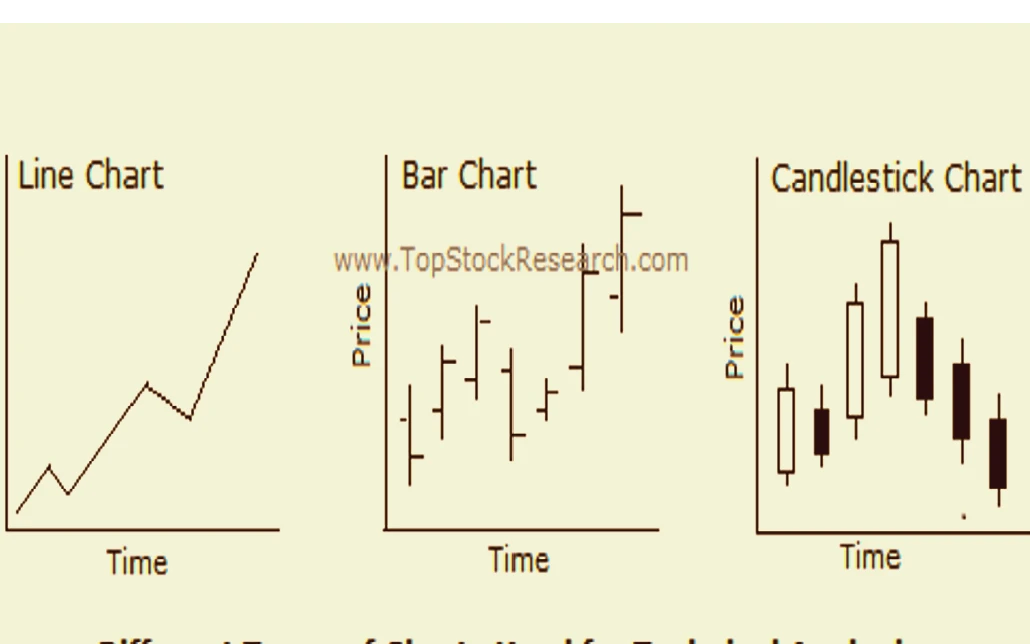
Chart Types in Technical Analysis
Different chart types provide various perspectives on price movements:
- Line Charts: Simple representation of closing prices over time.
- Bar Charts: Display opening, high, low, and closing prices for each period.
- Candlestick Charts: Provide more detailed information with visual patterns.
Each chart type has its advantages. Line charts offer a clear, straightforward view of price trends, while bar and candlestick charts provide more detailed insights into price action, including opening and closing prices and intraday highs and lows. Traders choose the chart type that best suits their analysis style and strategy.
Key Technical Indicators
Technical indicators help traders interpret price movements and identify trading opportunities:
- Moving Averages: Smooth out price data to identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Shows the relationship between two moving averages.
- Bollinger Bands: Indicate volatility and potential overbought or oversold conditions.
- Fibonacci Retracement: Identifies potential support and resistance levels.
These indicators can be used individually or in combination to provide a comprehensive view of market conditions. For instance, moving averages can help identify the direction of a trend, while RSI and MACD can signal potential entry and exit points based on market momentum.
Analyzing Chart Patterns
Chart patterns help traders identify potential reversal or continuation signals. Some common patterns include:
- Head and Shoulders: Indicates a potential reversal.
- Double Tops and Bottoms: Suggests a reversal of the current trend.
- Triangles: Show potential breakouts in the direction of the trend.
Recognizing these patterns can provide valuable insights into future price movements. For example, a head and shoulders pattern might signal the end of an uptrend, indicating a potential short-selling opportunity. Understanding and identifying these patterns is a key skill for technical traders.
Support and Resistance Levels
Support levels are price points where a currency tends to find buying interest, preventing it from falling further. Resistance levels are points where selling interest prevents the price from rising. Identifying these levels helps traders make informed decisions about entry and exit points.
Support and resistance levels can be identified using historical price data, technical indicators, and psychological price points. These levels provide valuable reference points for setting stop-loss and take-profit orders, helping traders manage their risk and maximize their profits.
Implementing Technical Analysis Strategies
To effectively use technical analysis, traders often combine multiple indicators and chart patterns to confirm their predictions. Backtesting strategies on historical data helps ensure their reliability before applying them to live trading.
Combining different indicators can provide a more comprehensive view of the market and increase the accuracy of trading signals. For example, a trader might use moving averages to identify the overall trend, while using RSI to confirm overbought or oversold conditions. Backtesting allows traders to refine their strategies and build confidence in their approach.
Popular Forex Trading Strategies
There are several forex trading strategies that traders use to navigate the market. Each strategy has its own set of rules, advantages, and disadvantages. Here are some of the most popular ones:
Scalping
Scalping involves making multiple trades throughout the day to profit from small price movements. Scalpers aim to make quick profits by entering and exiting the market within minutes or seconds.
Key Characteristics of Scalping
- High Frequency: Numerous trades are made within a short period.
- Small Profits: Each trade targets small price changes.
- Tight Spreads: Preferred on currency pairs with low spreads.
Scalping requires traders to be highly focused and quick in their decision-making. This strategy is best suited for those who can dedicate significant time to monitoring the markets and executing trades. Scalpers often use leverage to amplify their returns, making effective risk management crucial.
Tools and Indicators for Scalping
Scalpers use technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, and MACD to identify entry and exit points. They often trade during high liquidity periods to ensure quick execution and minimal slippage.
For example, a scalper might use short-term moving averages to identify trends and MACD to confirm momentum. Trading during major market sessions, such as the London or New York sessions, ensures sufficient liquidity and tighter spreads, which are critical for the success of scalping.
Pros and Cons of Scalping
Pros:
- Potential for quick profits.
- Less exposure to market risk.
- Suitable for volatile markets.
Cons:
- Requires intense concentration and quick decision-making.
- High transaction costs due to frequent trading.
- Can be stressful and demanding.
Day Trading
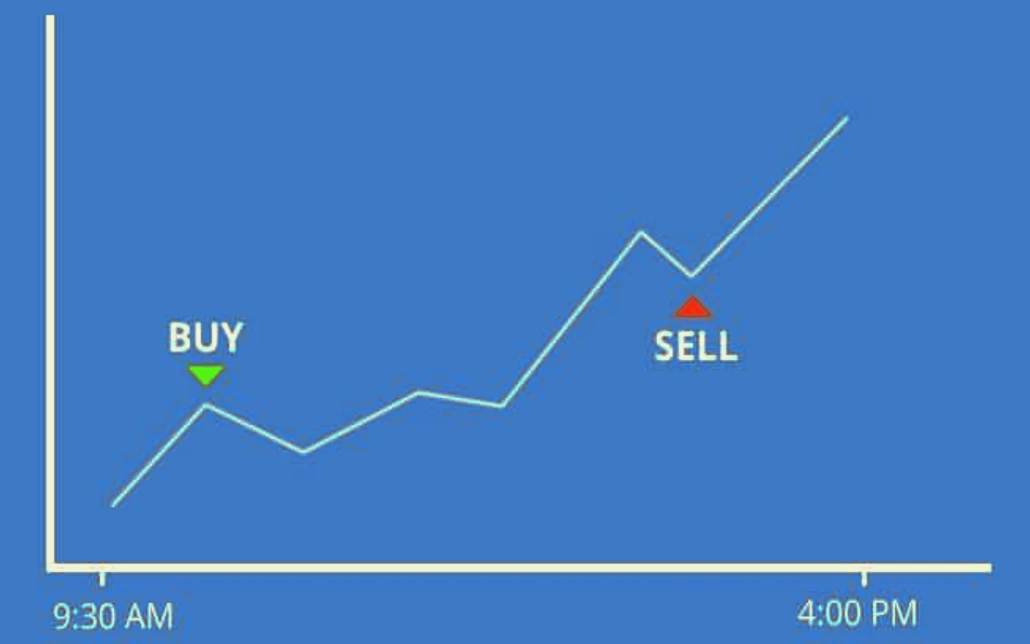
Day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day. Day traders avoid overnight risk by closing all trades before the market closes.
Key Characteristics of Day Trading
- Intraday Trading: No positions are held overnight.
- Moderate Frequency: Several trades are made within a day.
- Focus on Liquidity: Prefers highly liquid currency pairs.
Day trading requires a balanced approach, combining technical analysis with an understanding of fundamental factors. Day traders often rely on economic news and data releases to make informed trading decisions. This strategy is suitable for those who can dedicate significant time to analyzing the markets and executing trades throughout the day.
Tools and Indicators for Day Trading
Day traders use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis. They monitor economic news and use technical indicators like moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and pivot points to make trading decisions.
For instance, a day trader might use pivot points to identify key support and resistance levels, combined with moving averages to determine the trend direction. Economic news releases can create short-term volatility, providing opportunities for day traders to profit from price movements.
Pros and Cons of Day Trading
Pros:
- No overnight risk.
- Potential for consistent daily profits.
- Flexibility in trading hours.
Cons:
- Requires significant time and attention.
- Can be stressful due to market fluctuations.
- High transaction costs.
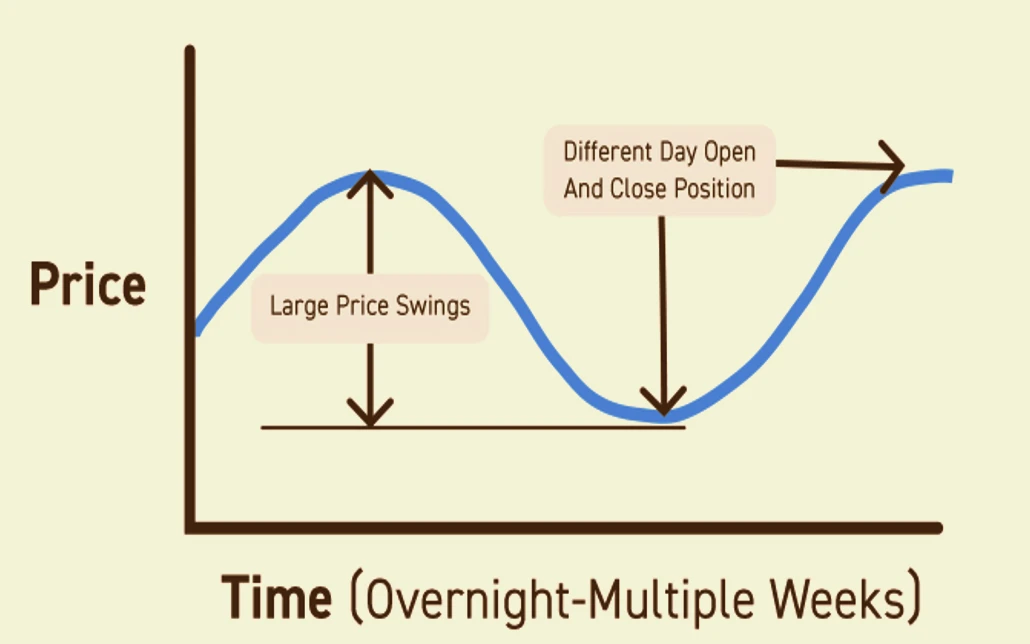
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, aiming to profit from price swings. Swing traders focus on short to medium-term market trends.
Swing Trading
Key Characteristics of Swing Trading
- Medium-Term: Positions are held for days to weeks.
- Trend Following: Focuses on capturing trend movements.
- Lower Frequency: Fewer trades compared to day trading.
Swing trading allows for more flexibility and requires less time commitment compared to day trading. Swing traders aim to capture larger price movements, benefiting from both trending and consolidating markets. This strategy is suitable for those who prefer a less intensive trading schedule.
Tools and Indicators for Swing Trading
Swing traders use technical analysis to identify trends and potential reversals. Indicators like moving averages, MACD, and Fibonacci retracement are commonly used. Fundamental analysis is also employed to understand broader market trends.
For example, a swing trader might use Fibonacci retracement levels to identify potential entry points during a pullback in a trending market. Combining this with MACD to confirm momentum can help increase the accuracy of trades. Swing traders also keep an eye on economic events that could impact market sentiment.
Pros and Cons of Swing Trading
Pros:
- Less time-intensive compared to day trading.
- Potential for significant profits from trend movements.
- Flexibility to trade part-time.
Cons:
- Exposure to overnight and weekend risk.
- Requires patience and discipline.
- Potential for missed opportunities due to longer holding periods.
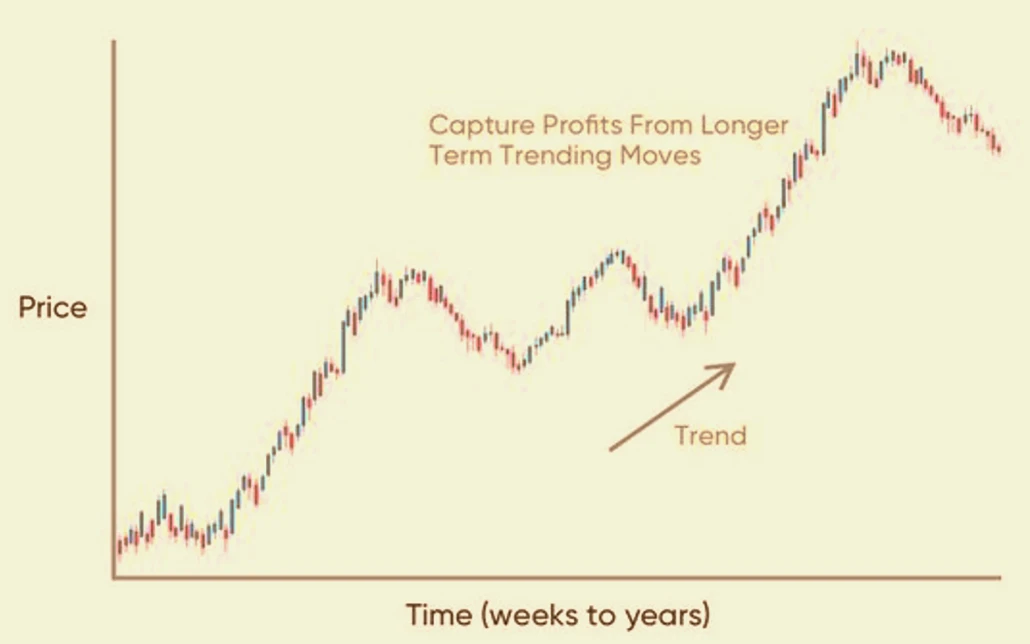
Position Trading
Position trading involves holding positions for weeks, months, or even years. Position traders focus on long-term trends and macroeconomic factors.
Key Characteristics of Position Trading
- Long-Term: Positions are held for an extended period.
- Fundamental Focus: Emphasis on economic and geopolitical factors.
- Low Frequency: Fewer trades with longer holding periods.
Position trading requires a deep understanding of fundamental analysis and a willingness to hold trades through market fluctuations. This strategy is suitable for those who have significant capital to invest and prefer a long-term approach to trading.
Tools and Indicators for Position Trading
Position traders rely heavily on fundamental analysis, including economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical events. Technical analysis is used to identify long-term trends and entry/exit points.
For instance, a position trader might analyze central bank interest rate policies and economic growth forecasts to make long-term trading decisions. Technical indicators such as moving averages can help confirm the overall trend direction and identify optimal entry and exit points.
Pros and Cons of Position Trading
Pros:
- Potential for substantial profits from long-term trends.
- Less time-intensive compared to shorter-term strategies.
- Lower transaction costs due to fewer trades.
Cons:
- Requires significant capital and patience.
- Exposure to long-term market risk.
- Can miss short-term opportunities.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Effective risk management is crucial for long-term success in forex trading. It involves strategies and techniques to minimize potential losses and protect trading capital.
Risk management helps traders stay in the market longer and avoid significant losses. It involves setting appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels, determining position sizes, and diversifying trades. By managing risk effectively, traders can maintain a stable trading performance and avoid catastrophic losses.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
- Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close a trade at a predetermined loss level.
- Take-Profit Orders: Automatically close a trade at a predetermined profit level.
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are essential tools for managing risk. They help traders limit potential losses and lock in profits without having to constantly monitor the market. By setting these orders at strategic levels, traders can manage their risk exposure and ensure that their trades align with their overall trading plan.
Position Sizing
Determining the appropriate position size based on account balance and risk tolerance is vital. Traders use various methods, such as fixed percentage risk and the Kelly criterion, to calculate position sizes.
Position sizing helps traders control the amount of risk they take on each trade. By limiting the amount of capital at risk to a small percentage of their overall account balance, traders can protect their capital and reduce the impact of losing trades. This approach allows for more consistent performance and reduces the likelihood of significant drawdowns.
Diversification
Diversifying trades across different currency pairs and strategies helps spread risk. By not putting all capital into a single trade, traders can mitigate potential losses.
Diversification reduces the impact of adverse market movements on a trader’s overall portfolio. By spreading risk across multiple trades and currency pairs, traders can achieve more stable returns and reduce the likelihood of significant losses. This approach is especially important in the volatile forex market.
Using Leverage Wisely
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. However, it amplifies both potential profits and losses. It’s essential to use leverage cautiously and understand its risks.
While leverage can increase potential returns, it also magnifies losses. Traders should use leverage judiciously and ensure that their position sizes are appropriate for their risk tolerance and account balance. Proper leverage management is crucial for long-term success in forex trading.
Keeping a Trading Journal
Maintaining a trading journal helps traders track their performance, identify patterns, and refine their strategies. Recording trades, reasons for entering/exiting, and outcomes provides valuable insights for improvement.
A trading journal allows traders to review their past performance and identify areas for improvement. By analyzing their trades and understanding what worked and what didn’t, traders can refine their strategies and make better-informed decisions in the future. Keeping detailed records is an important part of continuous learning and development.
Implementing a Risk Management Plan
Having a well-defined risk management plan ensures that traders stick to their risk tolerance levels. This plan should include rules for setting stop-loss orders, position sizing, and managing leverage.
A risk management plan helps traders stay disciplined and avoid emotional decision-making. By following a structured plan, traders can maintain consistent performance and protect their capital. This plan should be reviewed and adjusted regularly to ensure it remains effective in changing market conditions.
Psychological Aspects of Forex Trading
Trading psychology plays a significant role in a trader’s success. Emotions like fear, greed, and overconfidence can impact decision-making and lead to poor trading outcomes.
Managing emotions is crucial for maintaining a disciplined approach to trading. Emotional decision-making can lead to impulsive trades, excessive risk-taking, and significant losses. By understanding the psychological aspects of trading, traders can develop strategies to manage their emotions and make rational decisions.
Managing Emotions
- Fear: Fear of losing can lead to hesitation and missed opportunities. It’s essential to trust your analysis and strategy.
- Greed: Greed can lead to overtrading and taking unnecessary risks. Setting realistic profit targets helps manage greed.
- Overconfidence: Overconfidence can result in ignoring risk management rules. Staying humble and disciplined is crucial.
Recognizing and managing these emotions can help traders stay focused and make better trading decisions. For example, setting realistic profit targets can help manage greed, while trusting your analysis can reduce the impact of fear. Staying disciplined and following your trading plan is key to maintaining consistency.

Developing a Trading Plan
A well-structured trading plan provides a clear roadmap for making decisions. It includes entry and exit criteria, risk management rules, and guidelines for evaluating performance.
A trading plan helps traders stay organized and focused. By outlining specific criteria for entering and exiting trades, traders can avoid impulsive decisions and stick to their strategies. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure it remains effective in changing market conditions.
Staying Disciplined
Discipline is the cornerstone of successful trading. Sticking to your trading plan, managing risk, and avoiding impulsive decisions help maintain consistency and profitability.
Staying disciplined requires a strong commitment to following your trading plan and managing your emotions. By maintaining discipline, traders can avoid common pitfalls and achieve more consistent results. This involves adhering to risk management rules, setting realistic goals, and avoiding overtrading.
Learning from Mistakes
Every trader makes mistakes, but successful traders learn from them. Analyzing past trades, identifying errors, and making necessary adjustments lead to continuous improvement.
Learning from mistakes is an important part of a trader’s development. By reviewing past trades and understanding what went wrong, traders can refine their strategies and improve their decision-making. This process involves keeping detailed records, analyzing performance, and making adjustments as needed.
Seeking Support and Education
Joining trading communities, attending webinars, and reading educational resources provide valuable knowledge and support. Engaging with experienced traders and learning from their insights can enhance your trading skills.
Continuous education is crucial for staying competitive in the forex market. By seeking out educational resources and engaging with the trading community, traders can stay informed about market developments and improve their skills. This involves attending webinars, reading books and articles, and participating in forums and discussion groups.
Advanced Forex Trading Strategies
For experienced traders, advanced strategies offer opportunities to enhance profits and manage risks more effectively.
Advanced strategies involve more complex analysis and techniques, often requiring specialized knowledge and tools. These strategies can provide significant returns but also come with higher risks. Traders need to thoroughly understand these strategies and their potential implications before implementing them.
Carry Trade
The carry trade strategy involves borrowing in a currency with a low-interest rate and investing in a currency with a high-interest rate. Traders profit from the interest rate differential.
Key Characteristics of Carry Trade
- Interest Rate Differential: Focuses on currencies with significant interest rate differences.
- Long-Term: Positions are held for an extended period to benefit from interest payments.
- Low Volatility: Prefers stable economic conditions.
Carry trade is suitable for traders with a long-term perspective and a good understanding of macroeconomic factors. This strategy involves significant capital and requires careful risk management to protect against adverse currency movements.
Pros and Cons of Carry Trade
Pros:
- Potential for steady profits from interest rate differentials.
- Less reliance on price movements.
- Can be part of a diversified portfolio.
Cons:
- Exposure to exchange rate risk.
- Vulnerable to sudden market changes.
- Requires significant capital.
News Trading
News trading involves making trades based on economic news and data releases. Traders aim to profit from market volatility following major announcements.
Key Characteristics of News Trading
- High Volatility: Capitalizes on sharp price movements.
- Short-Term: Trades are typically held for a short duration.
- Focus on Major Events: Includes central bank meetings, employment reports, and GDP releases.
News trading requires quick decision-making and execution. Traders need to stay informed about scheduled economic events and understand their potential impact on the market. This strategy is suitable for those who can react quickly to market changes and manage risk effectively.
Tools and Techniques for News Trading
- Economic Calendars: Track upcoming news events.
- Price Alerts: Set alerts for significant price movements.
- Volatility Indicators: Identify periods of high volatility.
By using these tools, news traders can prepare for major events and capitalize on market volatility. For example, setting price alerts can help traders react quickly to significant movements, while volatility indicators can identify optimal trading opportunities.
Pros and Cons of News Trading
Pros:
- Potential for significant profits from rapid price movements.
- Clear entry and exit points based on news events.
- Opportunities for frequent trading.
Cons:
- High risk due to market unpredictability.
- Requires quick decision-making and execution.
- Can be stressful and demanding.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading involves using computer programs to execute trades based on predefined criteria. These algorithms can analyze market data, identify opportunities, and execute trades faster than human traders.
Key Characteristics of Algorithmic Trading
- Automated Execution: Trades are executed without human intervention.
- High Frequency: Can involve thousands of trades per day.
- Data-Driven: Relies on quantitative analysis and machine learning.
Algorithmic trading requires significant technical knowledge and resources. Traders need to develop and maintain their algorithms, ensuring they remain effective in changing market conditions. This strategy is suitable for those with a strong background in programming and quantitative analysis.
Tools and Technologies for Algorithmic Trading
- Trading Platforms: Software for developing and executing algorithms.
- API Access: Connects algorithms to trading platforms and market data.
- Backtesting Software: Tests algorithms on historical data.
By using these tools, traders can develop and refine their algorithms to improve performance. Backtesting software allows traders to test their strategies on historical data, ensuring their algorithms are robust and reliable.
Pros and Cons of Algorithmic Trading
Pros:
- Eliminates emotional decision-making.
- Can analyze large datasets quickly.
- Executes trades at optimal prices.
Cons:
- Requires technical knowledge and resources.
- Potential for technical failures and glitches.
- Can be expensive to develop and maintain.
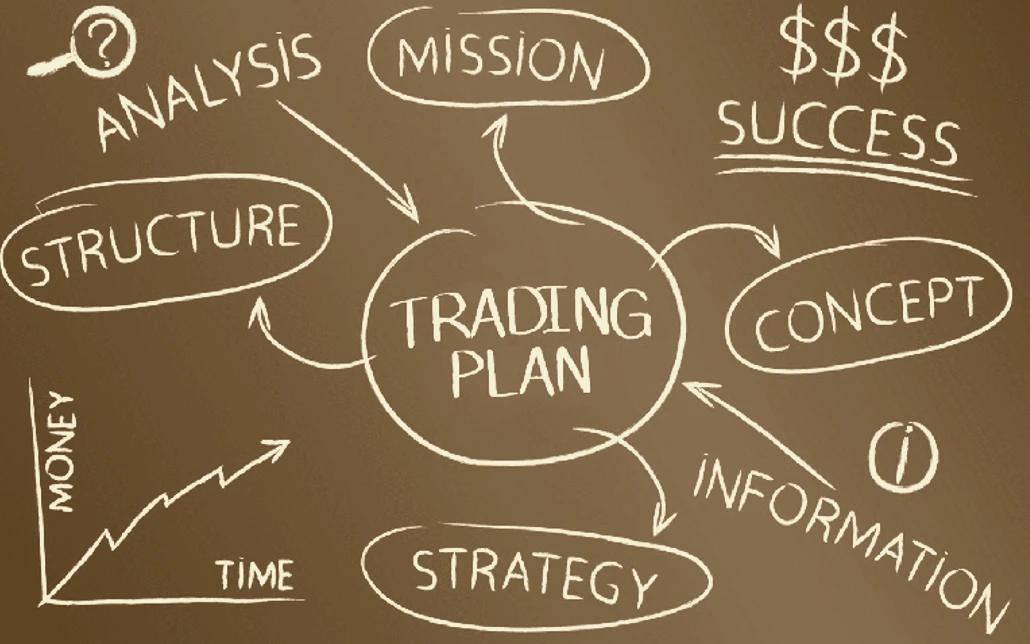
Creating a Forex Trading Plan
A well-defined trading plan is essential for long-term success. It provides a structured approach to trading, helping traders stay disciplined and focused.
A trading plan outlines specific criteria for entering and exiting trades, managing risk, and evaluating performance. By following a structured plan, traders can avoid impulsive decisions and maintain consistent performance. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure it remains effective in changing market conditions.
Components of a Trading Plan
- Trading Goals: Define short-term and long-term objectives.
- Risk Management: Outline risk tolerance, position sizing, and stop-loss rules.
- Market Analysis: Specify the methods and tools for analysis.
- Trade Execution: Detail entry and exit criteria.
- Performance Evaluation: Set benchmarks for evaluating success.
These components provide a comprehensive framework for making informed trading decisions. By setting clear goals and criteria, traders can stay focused and disciplined, avoiding common pitfalls and maintaining consistent performance.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting achievable goals helps maintain motivation and focus. Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Realistic goals provide a clear direction and help traders stay motivated. By setting specific and measurable objectives, traders can track their progress and make necessary adjustments. This approach ensures that goals are attainable and aligned with overall trading strategies.
Developing a Routine
Establishing a daily trading routine ensures consistency and discipline. This routine should include market analysis, trade execution, and performance review.
A consistent routine helps traders stay organized and focused. By dedicating specific times for market analysis and trade execution, traders can avoid impulsive decisions and maintain a disciplined approach. Regular performance reviews allow traders to identify areas for improvement and refine their strategies.
Continuous Learning
The forex market is constantly evolving, and continuous learning is crucial for staying competitive. Traders should regularly update their knowledge and skills through education and practice.
Continuous learning helps traders stay informed about market developments and improve their skills. This involves reading books and articles, attending webinars and workshops, and participating in trading communities. By staying updated, traders can adapt to changing market conditions and enhance their performance.
Reviewing and Refining the Plan
Regularly reviewing and refining the trading plan ensures it remains effective and aligned with market conditions. Traders should analyze their performance, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments.
Reviewing the trading plan allows traders to assess its effectiveness and make adjustments as needed. By analyzing past performance and identifying patterns, traders can refine their strategies and improve their decision-making. This continuous process of review and refinement is essential for long-term success.
FAQs
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, involves buying and selling currencies to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. It is the largest financial market globally, with a daily turnover exceeding $6 trillion. Traders use various strategies and tools to navigate this dynamic market. The goal is to capitalize on the changes in currency values relative to one another.
The forex market includes several key participants, each playing a distinct role. Central banks influence currency prices through monetary policy and interventions, often aimed at stabilizing their respective economies. Commercial banks facilitate transactions for clients and themselves, acting as market makers by providing liquidity. Hedge funds engage in speculative trading to generate profits, often using leverage to amplify their returns. Corporations conduct currency transactions for international trade, seeking to hedge against foreign exchange risk. Lastly, retail traders, or individual investors, trade for personal profit, utilizing various online trading platforms to access the market.
In forex trading, currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY. The first currency in the pair is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency. The exchange rate indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency. For instance, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.2000, it means one Euro is worth 1.20 US Dollars. This system allows traders to speculate on the relative strength of one currency against another, providing numerous trading opportunities.
Fundamental analysis in forex trading involves evaluating a country’s economic indicators, political stability, and overall economic health to predict currency movements. Key economic indicators include interest rates, GDP, employment data, inflation rates, and trade balance. Interest rates are adjusted by central banks to control inflation and stabilize the economy, influencing currency values. GDP measures the total economic output of a country, providing insight into economic growth. Employment data reflects the health of the labor market, while inflation rates indicate the rate at which prices are rising. Trade balance shows the difference between a country’s exports and imports, impacting currency demand and supply.
Technical analysis involves studying historical price charts and using various indicators to predict future price movements. Different chart types provide various perspectives on price movements, including line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts. Key technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI, MACD, Bollinger Bands, and Fibonacci retracement help traders interpret price movements and identify trading opportunities. Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, and triangles, assist in identifying potential reversal or continuation signals. Support and resistance levels are price points where currencies tend to find buying or selling interest, guiding traders on entry and exit points.
Scalping involves making multiple trades throughout the day to profit from small price movements. Scalpers aim to make quick profits by entering and exiting the market within minutes or seconds, requiring intense concentration and quick decision-making. Day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day, avoiding overnight risk. Day traders often rely on economic news and data releases to make informed trading decisions. Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, aiming to profit from price swings. Swing traders focus on capturing trend movements, requiring patience and discipline. Position trading involves holding positions for weeks, months, or even years, focusing on long-term trends and macroeconomic factors. Position traders rely heavily on fundamental analysis and have a long-term perspective.
Risk management is crucial for long-term success in forex trading. It involves setting appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels, determining position sizes, and diversifying trades. Effective risk management helps traders stay in the market longer and avoid significant losses. Stop-loss orders automatically close trades at predetermined loss levels, while take-profit orders lock in profits at predetermined levels. Position sizing involves determining the appropriate size of each trade based on account balance and risk tolerance, using methods such as fixed percentage risk and the Kelly criterion. Diversification spreads trades across different currency pairs and strategies to mitigate risk.
Trading psychology plays a significant role in a trader’s success. Emotions like fear, greed, and overconfidence can impact decision-making and lead to poor trading outcomes. Managing emotions is crucial for maintaining a disciplined approach to trading. Fear of losing can lead to hesitation and missed opportunities, while greed can result in overtrading and taking unnecessary risks. Overconfidence can cause traders to ignore risk management rules. Developing a well-structured trading plan, staying disciplined, and learning from mistakes are essential for managing emotions and making rational decisions. Seeking support and continuous learning also help traders improve their psychological resilience.
Algorithmic trading involves using computer programs to execute trades based on predefined criteria. These algorithms analyze market data, identify opportunities, and execute trades faster than human traders. Automated execution eliminates emotional decision-making, allowing for more consistent performance. High-frequency trading can involve thousands of trades per day, relying on quantitative analysis and machine learning. Algorithmic trading requires significant technical knowledge and resources, including trading platforms for developing and executing algorithms, API access to connect algorithms to trading platforms and market data, and backtesting software to test algorithms on historical data. This approach can be expensive to develop and maintain but offers substantial benefits in speed and accuracy.
Creating a well-defined trading plan is essential for long-term success. A trading plan should include trading goals, risk management rules, market analysis methods, trade execution criteria, and performance evaluation benchmarks. Trading goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), helping traders maintain motivation and focus. Risk management outlines risk tolerance, position sizing, and stop-loss rules. Market analysis specifies the methods and tools for analysis, while trade execution details entry and exit criteria. Performance evaluation sets benchmarks for evaluating success, allowing traders to review and refine their strategies regularly.
Continuous learning is crucial for staying competitive in the forex market. Traders can join trading communities, attend webinars and workshops, read books and articles on forex trading, and engage with experienced traders for insights and advice. Educational resources provide valuable knowledge and support, helping traders stay informed about market developments and improve their skills. Mentorship from experienced traders can also enhance trading skills and provide guidance on navigating emotional challenges. By seeking out educational resources and staying informed, traders can enhance their performance and achieve long-term success in the dynamic forex market.
Conclusion
Mastering forex trading strategies requires a combination of knowledge, discipline, and continuous learning. By understanding the fundamental and technical aspects of the market, employing effective trading strategies, and managing risks, traders can enhance their chances of success. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, developing a well-structured trading plan and staying committed to it will help you navigate the complexities of the forex market and achieve your trading goals.
By following the principles outlined in this guide, traders can develop a comprehensive approach to forex trading, combining fundamental and technical analysis with effective risk management and disciplined trading practices. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying competitive and achieving long-term success in the dynamic forex market.mmitted to it will help you navigate the complexities of the forex market and achieve your trading goals.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!