The Concept of Leverage in Forex
Leverage in forex trading allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, significantly enhancing the potential for profit. By borrowing funds from a broker, traders can engage in trades that would otherwise be inaccessible due to capital constraints. However, while leverage can amplify profits, it also poses considerable risks, including the potential for significant losses.
Understanding leverage is essential for anyone looking to navigate the forex market. It involves both margin requirements and the inherent risks associated with trading on borrowed capital. With the right knowledge and strategies, traders can leverage their positions effectively while managing the risks that come with it.
Contents
What is Leverage in Forex?
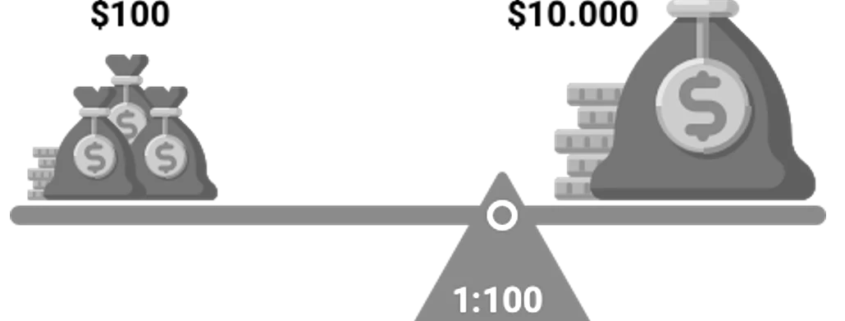
Leverage in forex is a financial tool that enables traders to magnify their trading capacity. By using leverage, traders can enter positions much larger than their initial capital outlay. For example, a leverage ratio of 100:1 allows a trader to control a position worth $100,000 with only $1,000 of their own money. This ability to borrow capital increases potential returns but also magnifies risks.
When trading with leverage, it is crucial to understand how it impacts both potential gains and losses. If a trader uses leverage to buy a currency pair and the market moves favorably, the profits can be substantial relative to the initial investment. Conversely, if the market moves against the trader, the losses can quickly exceed the initial investment, leading to margin calls or account liquidation.
Traders must also consider the margin requirement, which is the amount of capital needed to open and maintain a leveraged position. Different brokers may have varying margin requirements, which can affect the leverage ratios available to traders.
Leverage and Margin Explained
Margin is the amount of money that a trader needs to deposit to open a leveraged position. It serves as a security for the broker, ensuring that the trader can cover potential losses. The margin requirement is expressed as a percentage of the full position size. For instance, if the margin requirement is 2%, a trader would need to deposit $2,000 to open a $100,000 position.
The concept of margin is essential for understanding how leverage works in forex trading. When traders utilize leverage, they are essentially using borrowed funds to increase their exposure to the market. While this can lead to significant profits, it also entails a higher level of risk. If the market moves against a trader’s position, losses can accumulate quickly, potentially leading to a situation where the trader cannot meet the margin requirement.
Additionally, brokers may use a margin call to alert traders when their equity falls below a certain threshold. This warning gives traders an opportunity to either deposit additional funds or close positions to avoid liquidation. Understanding the relationship between margin and leverage is critical for effective risk management in forex trading.
How Leverage Works in Forex Trading
Leverage operates by allowing traders to open larger positions than they could with their available capital. When a trader opens a position using leverage, they are essentially borrowing funds from their broker. This process involves a margin account, where the broker holds a percentage of the total trade value as collateral.
For example, if a trader wants to purchase a currency pair valued at $50,000 with a leverage of 50:1, they would only need to deposit $1,000 as margin. This allows the trader to benefit from price movements in the currency pair without needing to have the entire $50,000 in their trading account.
The impact of leverage becomes evident in both profit and loss scenarios. If the currency pair appreciates by 1%, the trader would gain $500 on the $50,000 position, a 50% return on their initial $1,000 investment. Conversely, if the currency pair depreciates by 1%, the trader would incur a loss of $500, representing a 50% loss of their initial capital. This highlights the importance of careful risk management when trading with leverage.
Risks of Trading with Leverage
While leverage can enhance potential profits, it also introduces significant risks. One of the primary risks associated with leverage is the possibility of a margin call. If the market moves against a trader’s position and their account balance falls below the required margin level, the broker may require additional funds to maintain the position. Failure to meet this requirement can lead to automatic liquidation of the position, resulting in substantial losses.
Another risk is the emotional stress that comes with trading on leverage. The potential for quick gains or losses can lead to impulsive decision-making, which may negatively impact a trader’s strategy. The psychological effects of trading with leverage can create a cycle of fear and greed, making it challenging to stick to a well-defined trading plan.
Finally, the volatility of the forex market can exacerbate the risks associated with leverage. Currency prices can fluctuate rapidly due to economic news, geopolitical events, or changes in market sentiment. Traders using high leverage must be prepared for the possibility of large swings in their account balance, which can lead to rapid losses.

Benefits of Using Leverage in Forex
Despite the risks, leverage offers several benefits that make it an attractive option for many forex traders. One of the primary advantages is the ability to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This means that traders can potentially generate higher returns on their investments, making leverage a powerful tool for those who manage risk effectively.
Leverage also allows traders to diversify their trading strategies without needing significant capital. By using leverage, traders can open multiple positions across different currency pairs, spreading their risk and increasing their chances of profitability. This diversification can be particularly beneficial in a highly liquid market like forex, where opportunities can arise quickly.
Additionally, leverage can enhance the overall trading experience. For many traders, the excitement of the forex market is amplified by the potential for rapid gains. This can lead to increased engagement and motivation, encouraging traders to develop and refine their strategies over time.
Choosing the Right Leverage Ratio
Selecting the appropriate leverage ratio is a critical aspect of forex trading. Different traders have varying risk tolerances, trading styles, and capital allocations, which means that the optimal leverage ratio can differ significantly from one trader to another.
For conservative traders, lower leverage ratios may be more appropriate. A ratio of 2:1 or 5:1 can help minimize the risk of significant losses while still providing opportunities for profit. These traders may prefer to take fewer risks and focus on long-term strategies, prioritizing capital preservation.
On the other hand, more aggressive traders may opt for higher leverage ratios, such as 50:1 or even 100:1. While this can lead to higher potential profits, it also significantly increases the risk of substantial losses. Traders who choose higher leverage must be disciplined in their risk management strategies to avoid catastrophic losses.
Ultimately, the choice of leverage ratio should align with a trader’s overall risk management plan, trading goals, and market conditions. It is essential to evaluate one’s financial situation and trading experience before selecting a leverage ratio that suits their needs.
Leverage and Trading Strategies
Incorporating leverage into trading strategies can enhance overall performance if executed properly. Successful traders often develop specific strategies tailored to their risk tolerance and market conditions. These strategies typically involve careful analysis of market trends, technical indicators, and economic news to identify optimal entry and exit points.
For instance, a trader using a trend-following strategy may employ leverage to capitalize on strong market movements. By opening leveraged positions in the direction of the trend, traders can amplify their potential gains. However, they must also be vigilant about market reversals, as a sudden change in direction can lead to significant losses.
Alternatively, some traders might use leverage in conjunction with risk management techniques, such as stop-loss orders. By setting predetermined exit points, traders can protect their capital while still benefiting from the potential upside of leveraged positions. This approach allows for a more structured trading experience, reducing the emotional toll that can accompany leveraged trading.
The Role of Forex Brokers in Leverage
Forex brokers play a crucial role in determining the leverage available to traders. Each broker has its own policies regarding margin requirements and leverage ratios, which can vary based on the trader’s location, account type, and trading volume. It is essential for traders to research and compare brokers to find one that aligns with their trading goals.
Additionally, brokers provide essential tools and resources for managing leveraged trades. Many brokers offer trading platforms equipped with advanced charting tools, economic calendars, and risk management features, allowing traders to make informed decisions. Access to educational resources can also help traders understand the implications of leverage and improve their overall trading strategies.
When selecting a broker, traders should also consider factors such as execution speed, spreads, and customer support. A reliable broker can enhance the trading experience and help mitigate some of the risks associated with leveraged trading.
FAQs
Leverage is expressed as a ratio, such as 50:1 or 100:1. This ratio indicates how much larger your trading position can be compared to your initial investment. For example, with 100:1 leverage, a $1,000 deposit allows you to control a $100,000 position.
While leverage can magnify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. If the market moves against your position, you could lose more than your initial investment, potentially leading to a margin call or liquidation of your account.
Managing leverage risks involves using appropriate position sizing, setting stop-loss orders, and avoiding excessive leverage. Educating yourself on market dynamics and maintaining disciplined trading strategies can also help mitigate risks.
Choosing the right leverage depends on your trading style, risk tolerance, and market knowledge. It’s advisable to start with lower leverage ratios until you gain more experience, allowing you to manage risks more effectively.
Not necessarily. While high leverage can increase potential profits, it also amplifies risk. It’s crucial to strike a balance between leverage and risk management to ensure sustainable trading success.
The maximum leverage offered by brokers varies by jurisdiction and regulatory requirements. In some regions, brokers may offer leverage ratios as high as 500:1, while others may limit it to lower levels to protect traders from excessive risk.
Conclusion
Leverage in forex trading is a double-edged sword. It offers the potential for significant profits but also comes with considerable risks. Understanding the mechanics of leverage, margin requirements, and effective risk management strategies is essential for successful trading. By choosing the right leverage ratio, developing sound trading strategies, and selecting a reputable broker, traders can navigate the complexities of the forex market while maximizing their opportunities for success.
Additional Resources
- Forex Leverage Calculator: A tool for calculating potential profits and margin requirements based on different leverage ratios.
- Educational Courses: Resources that provide in-depth knowledge about trading strategies, risk management, and market analysis.
- Broker Comparisons: Websites that compare different forex brokers based on leverage, spreads, and trading platforms.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!